World’s first long-term dialysis patient was treated on an artificial kidney at the University of Washington Hospital
On Mar. 9, 1960, In Seattle the world’s first long-term dialysis patient Clyde Shields was treated on an…
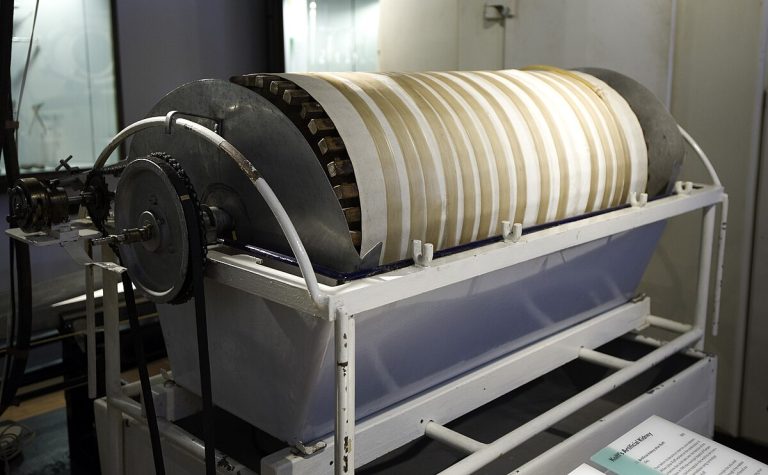

On Mar. 9, 1960, In Seattle the world’s first long-term dialysis patient Clyde Shields was treated on an…
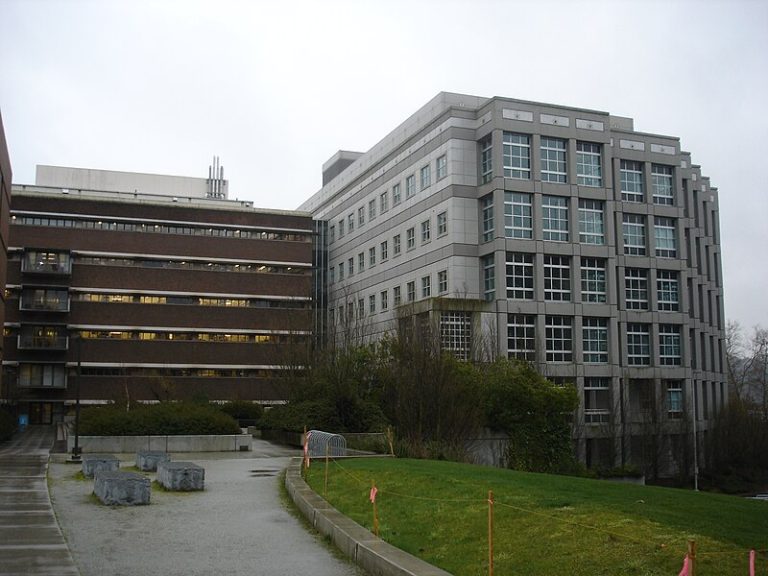

On May 4, 1959, the first major addition to the University of Washington Health Sciences Building, an eight-story,…

In 1959, Lester R. Sauvage, MD founded the Reconstructive Cardiovascular Research Laboratory as a branch of Providence Seattle…

In 1959, Min Chueh Chang pioneered in vitro fertilization. He was also co-inventor of the oral contraceptive pill….

In 1959, the Salk Institute was initially envisioned by Jonas Salk, M.D., the developer of the polio vaccine,…

In 1959, Arnel Hallauer became director of Iowa State University’s (ISU) maize breeding program. Hallauer was part of…

In 1958, the National Seed Storage Laboratory (NSSL), the first long-term seed storage facility in the world, opened…

On Oct. 19, 1956, the Pacific Northwest Diabetes Research Institute (PNDRI) was founded by William B. Hutchinson, Sr.,…
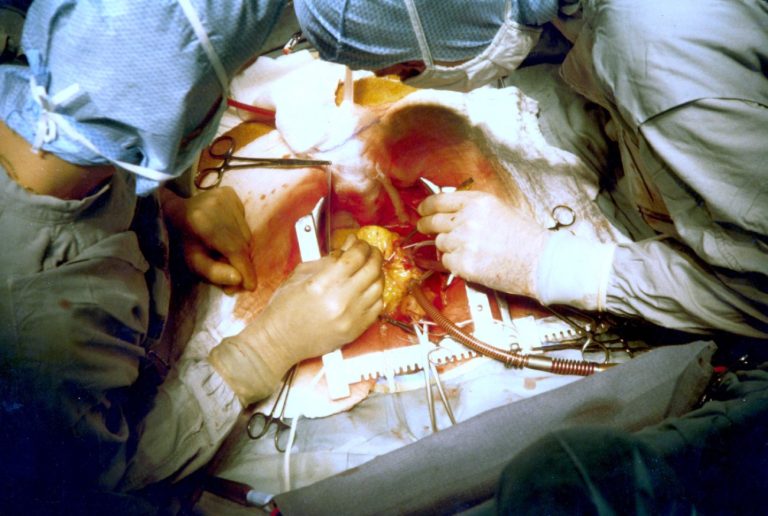
On Aug. 1, 1956, Dr. K. Alvin Merendino at the University of Washington in Seattle performed the first successful…

In 1956, seven students participated in the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation Summer Scholar Program which was originated by…

In Jul. 1955, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the U.S. Forest Service (USFS) sprayed DDT as…
On Apr. 26, 1955, Officials first noticed an increase in reported polio cases in California. Soon it was…

On Apr. 12, 1955, a convocation was held at the University of Michigan (UM), where Dr. Thomas Francis…

In 1955, the Division of Biologics Control (DBS) became an independent entity within the National Institutes of Health…

In 1955, The Mayo Clinic Heritage Hall museum opened in Rochester, Minnesota with a generous gift from John…

In 1955, Canada contributed to the safe cultivation of the poliovirus, using Medium 199, and an incubation process…

In 1955, geneticist Dr. James Bowman studied favism, the deficiency of glucose-6-dehydrogenase, in Iran. Favism is an acute…
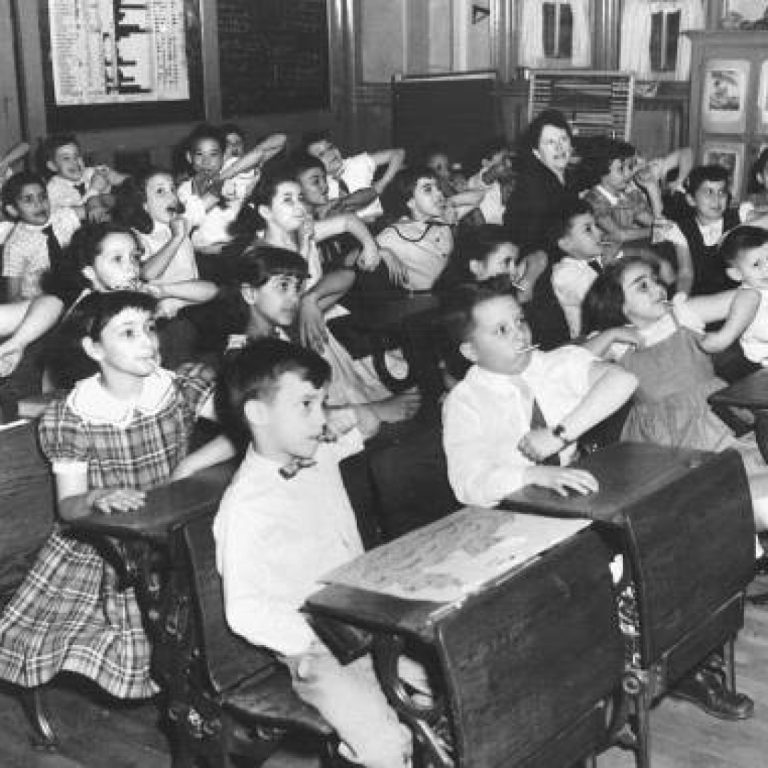

On Apr. 26, 1954, the largest controlled Polio vaccine field trial in the history of medicine got under…

On Apr. 25, 1954, the Vaccine Advisory Committee of the National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis, now known as…

On Mar. 26, 1954, Dr. C. Walton Lillehei at the University of Minnesota performed the world’s first open-heart…
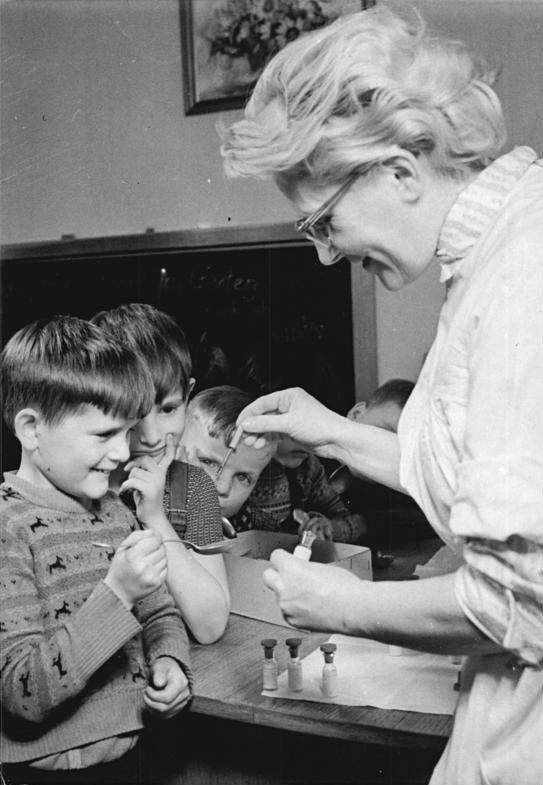

On Feb. 23, 1954, the first mass inoculation of the new Polio vaccine, developed by Dr. Jonas Salk…
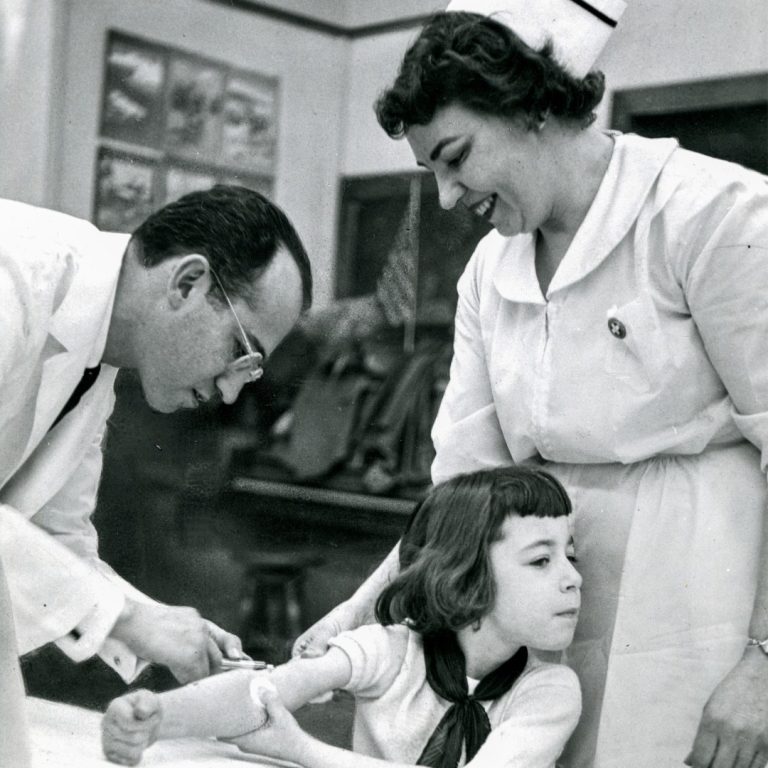

In February 1954, first-, second- and third-grade students from five suburban schools were the first to be inoculated…

In 1954, John Franklin Enders and Thomas C. Peebles isolated measles virus from an 11-year-old boy, David Edmonston….

In 1954, The McLaughlin Research Institute began with the arrival of Dr. Ernst Eichwald, recruited as a pathologist…

In 1954, Dr. Mary Carpenter became the first female member of Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation (OMRF) scientific staff…
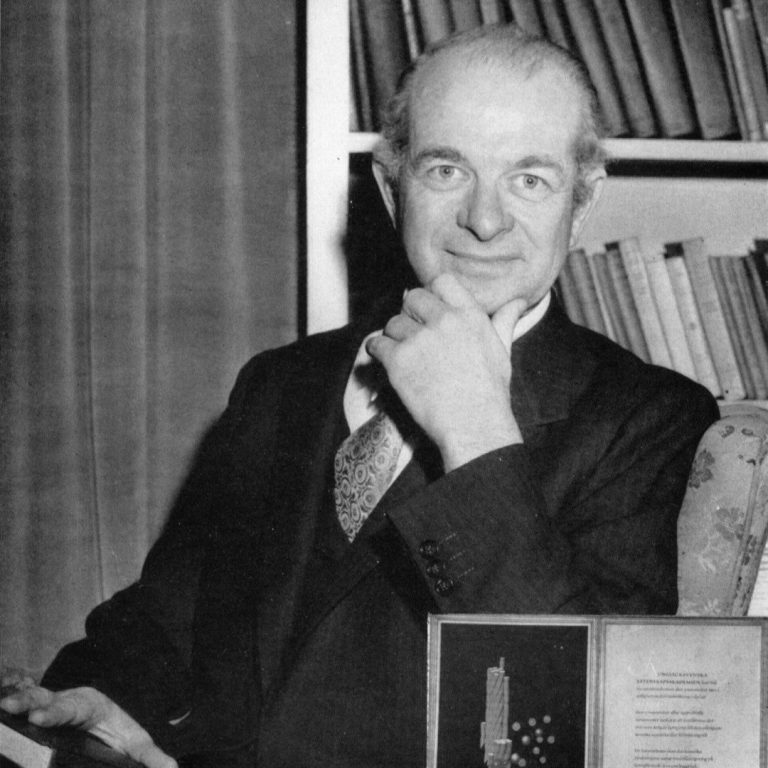

In 1954, Linus Carl Pauling (B.Sc., Chemical Engineering, Oregon State University, 1922) was awarded the Nobel Prize for…

In 1954, Dr. Jonas Salk and associates develop a potentially safe injectable vaccine against polio given to nearly…
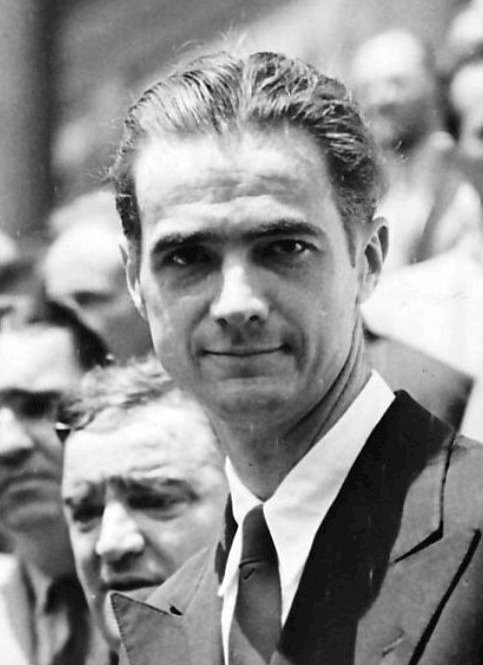

On Dec. 17, 1953, Howard Hughes signed documents that created the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, formed with the…

On May 16, 1953, Dr. Jonas Salk initiated the first community-based pilot trial of the Polio vaccine in…

On Apr. 25, 1953, Nature published James Watson’s and Francis Crick’s 900-word manuscript describing the double helical structure…