Regulation of Biologics–including serums, vaccines, and blood products–was transferred from NIH to FDA
On Jul. 1, 1972, the Regulation of Biologics–including serums, vaccines, and blood products–was transferred from the NIH to…

On Jul. 1, 1972, the Regulation of Biologics–including serums, vaccines, and blood products–was transferred from the NIH to…

In 1972, the Division of Biologics Standards was transferred from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to the U.S….

In 1972, by action of the Nebraska Legislature, the Eppley Cancer Center became an independent research institute with…

On Dec. 23, 1971, the National Cancer Act enacted by President Richard Nixon as part of the nation’s…

In 1971, the Public Health Service (PHS) Bureau of Radiological Health was transferred to U.S. Food and Drug…
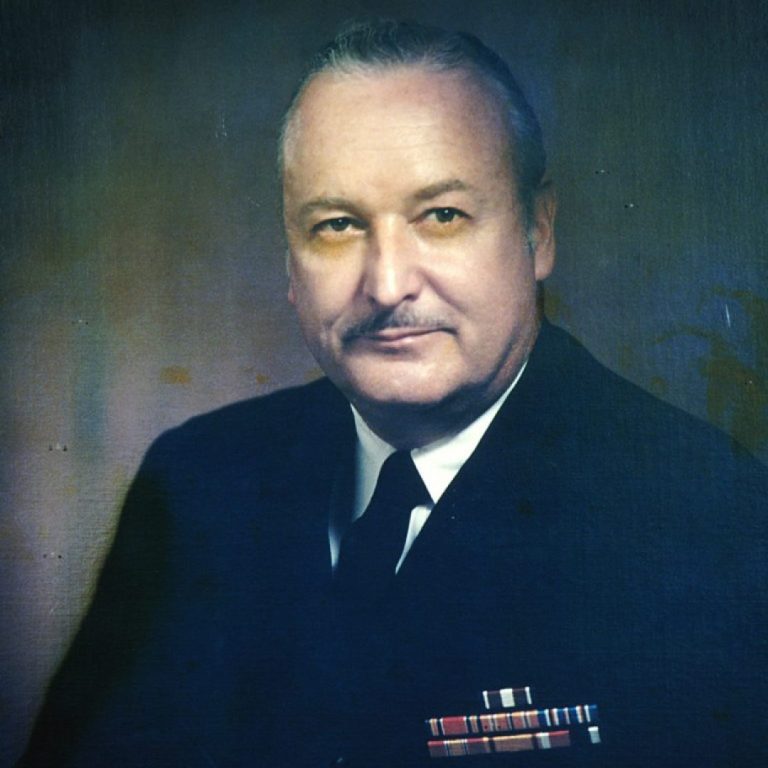

On Jul. 13, 1970, Carl Gwin Baker became the sixth director of the National Cancer Institute, serving until…

In 1966, the Drug Efficacy Study of the National Research Council’s Division of Medical Sciences, which was tasked…

In 1966, Mark Hatfield served in the State Legislature from 1951-1957; was secretary of state from 1957-1959. He…
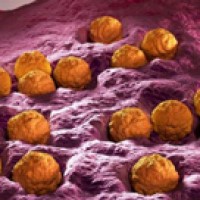
In 1965, the rubella virus was attenuated by a NIH research team lead by Paul Parkman and Harry…

In March 1964, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) to the U.S. Public Health Service was formed to…

In 1963, the U.S. Congress established the Immunization Grant Program; polio incidence plummeted to only 396 reported cases…

In 1962, oral polio vaccine types 1 and 2, developed by Dr. Albert Sabin and grown in monkey…

On Jan. 12, 1961, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) established the Laboratory of Viral Oncology, a new intramural…

In 1960, The Eppley Cancer Center, now a National Cancer Institute Laboratory Cancer Research Center, began in the…

In 1958, Arvid Carlsson discovered that levodopa (L-Dopa) was effective in treating the symptoms of Parkinsonism. a treatment…

From 1955 through early 1963, millions of people were accidentally exposed to simian virus 40 (SV40) as a…

In 1955, the Division of Biologics Control (DBS) became an independent entity within the National Institutes of Health…
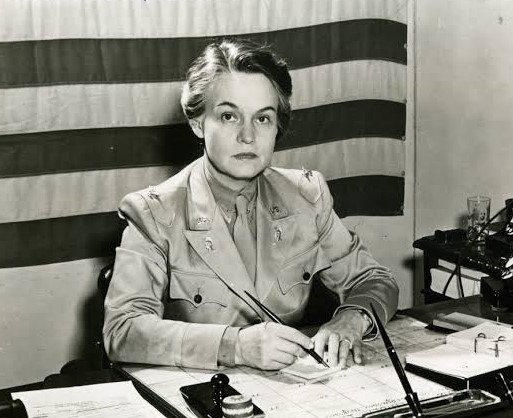

In 1955, Oveta Culp Hobby, the first Secretary of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW) appointed a committee of…

In 1954, first large-scale radiological examination of food carried out by U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) when…
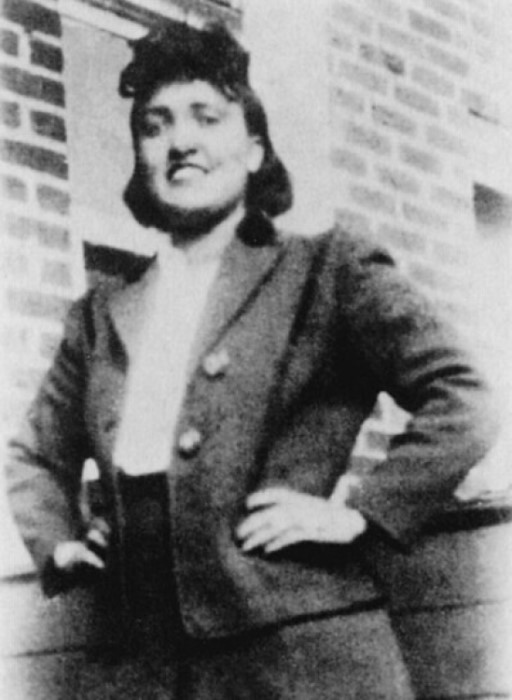

On Feb. 8, 1951, Henrietta Lacks, a tobacco farmer from Virginia died from cervical cancer, and a scientist…

In 1950, Robert W. Berliner of the NIH conducted work on renal physiology that led to a new…

In 1950, Earl Stadtman of the NIH discovered phosphotransacetylose, elucidating the role of acetyl CoA in fatty acid…

In 1948, the National Institute of Health was reorganized into the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and Rocky…

In 1946, the Research Grants Office was created at NIH in January to administer the Office of Scientific…

In 1945, Karl Habel cultivated mumps virus in embryonated eggs and devised serological tests for its presence. Habel…

In 1945, W. Ray Bryan, Michael B. Shimkin, Howard B. Andervont, Herbert Kahler and Thelma B. Dunn published…
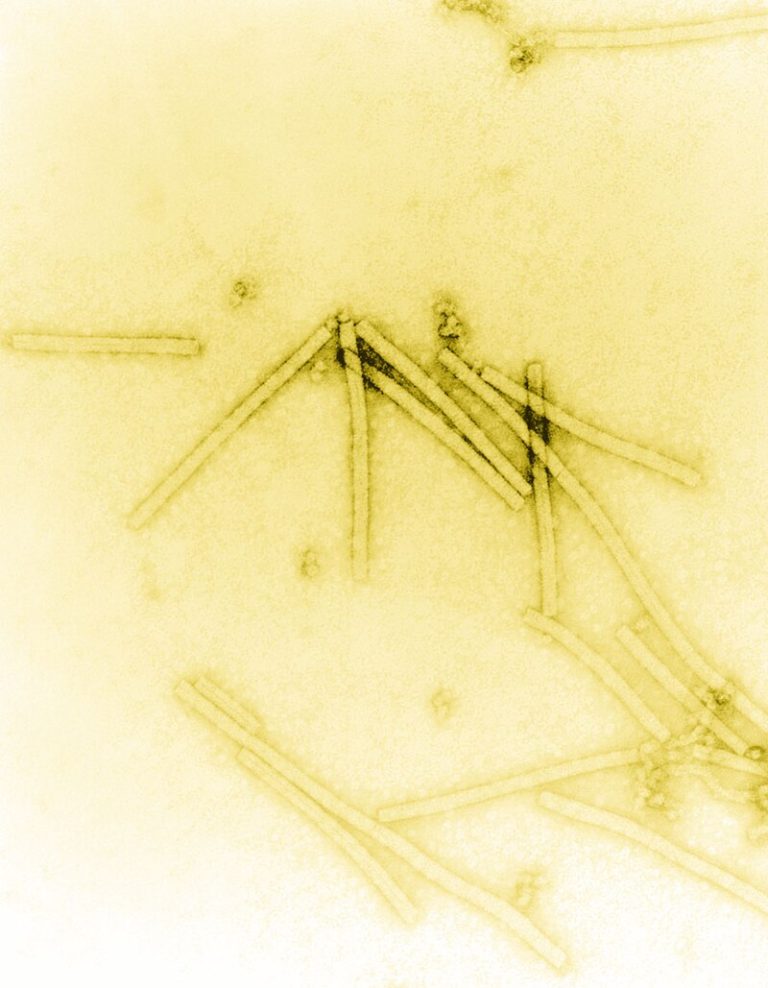
In 1945, scientists Ralph W. G. Wyckoff of the University of Michigan Department of Epidemiology and Robley Williams…

On Jul. 1, 1944, the Public Health Service Act, P.L. 410, 78th Congress, provided that “The National Cancer…
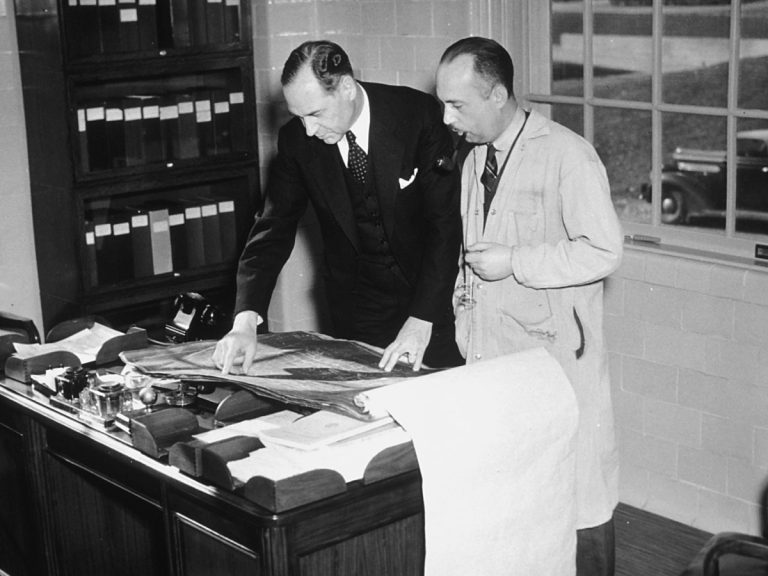

On Sept. 4, 1943, Dr. Carl Voegtlin resigned as director of the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Dr. Voegtlin…

In 1942, Willard H. Wright, Eloise Cram, Walter Newton and their colleagues in the NIH Division of Zoologye…