Stanford researchers discovered that the p53 protein works as an ’emergency brake’ on cancer development
On Jan. 2, 1996, Stanford Medicine researchers announced they had discovered that the p53 protein, known to be…
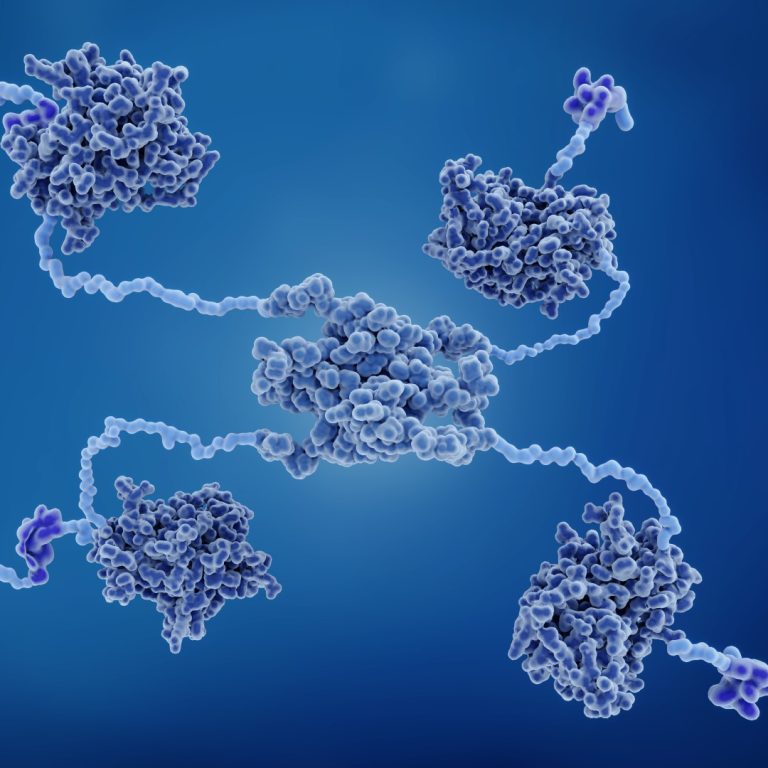
On Jan. 2, 1996, Stanford Medicine researchers announced they had discovered that the p53 protein, known to be…
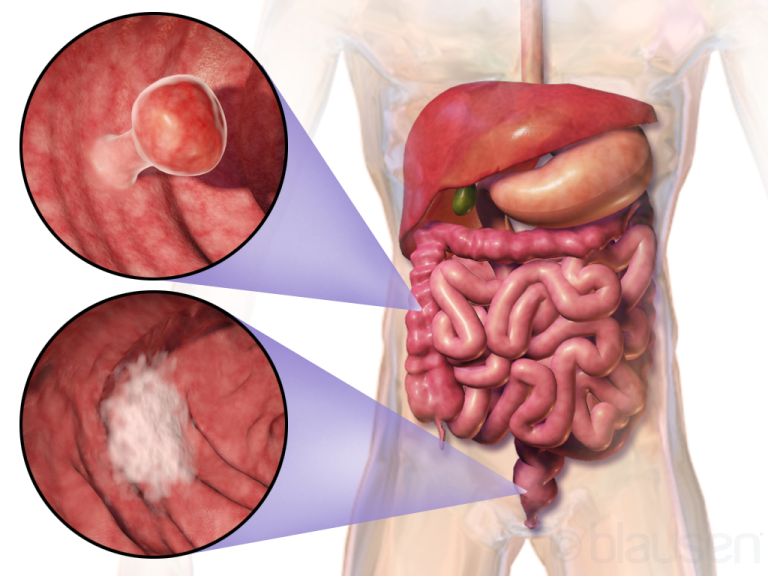
In June 1996, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) first approved irinotecan for the treatment of patients with…
In 1996, the American Cancer Society reported that the overall age-adjusted cancer mortality rate declined in each succeeding…
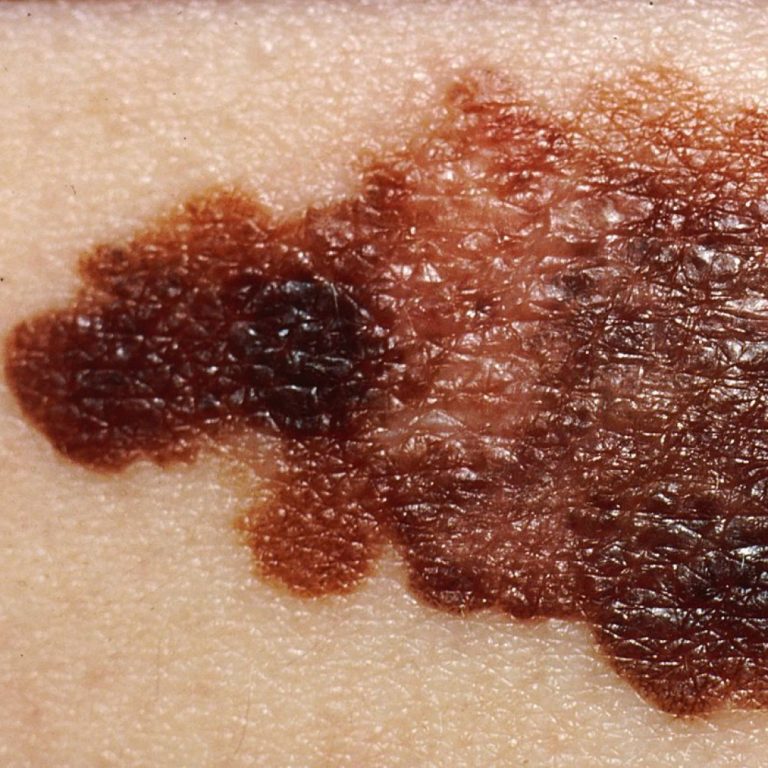
In 1996, Stanford Medicine developmental biologist Matthew Scott and a team at University of California, San Francisco discovered…

In 1996, the National Cervical Cancer Coalition (NCCC), a growing coalition of people battling cervical cancer and HPV…

In 1996, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found evidence of tobacco smoke exposure in…

In 1996, the University of Hawaii Cancer Center (UH) received National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designation, an honor it has…

In 1996, the University of Maryland Cancer Center was renamed Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center. In…

In 1996, the University of Maryland cancer programs moved to a private facility and renamed the University of…

In 1996, the Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center (SKCC) at Johns Hopkins University received National Cancer Institutes (NCI). The…

In 1996, Dr. Brenda Gallie identified the cause of drug-resistant childhood cancer of the retina, leading to an…

On Dec. 9, 1995, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved tretinoin, a differentiating agent related to…
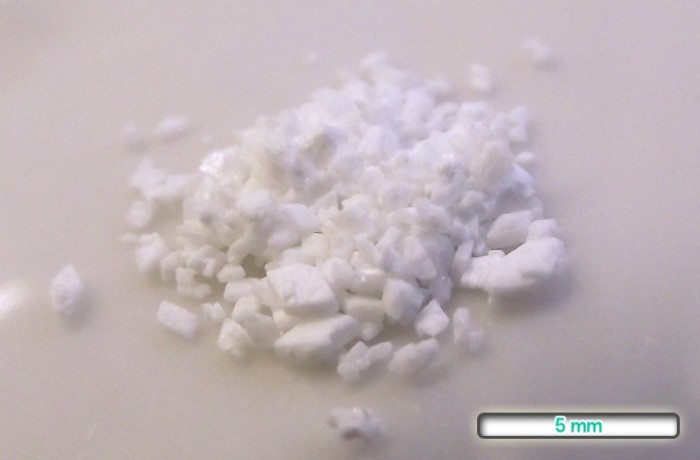

On Dec. 6, 1995, the U.S. Congress repealed the saccharin notice requirements. The store warning notice requirement was…
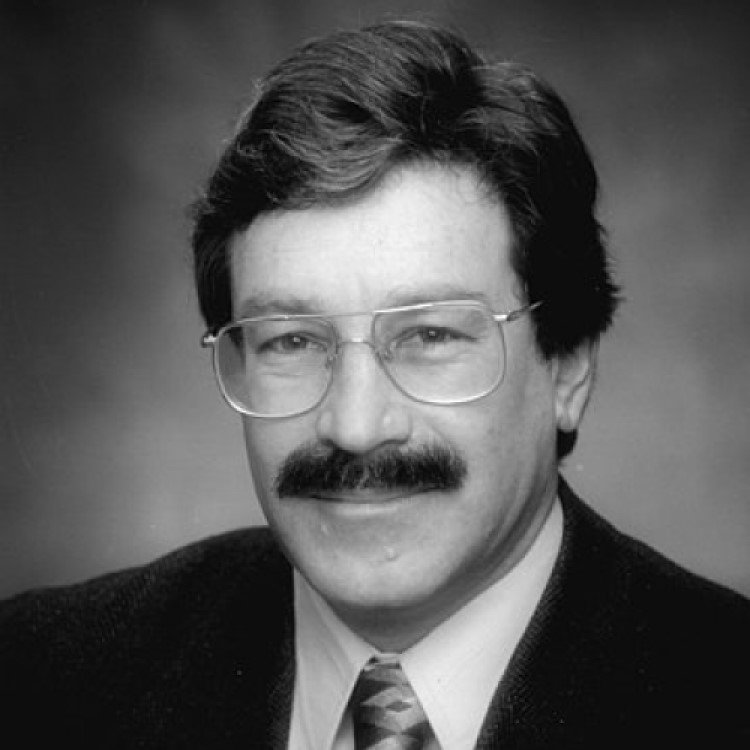

On Aug. 1, 1985, Richard D. Klausner became the eleventh director of the National Cancer Institute, serving until…

On Jul. 30, 1995, Peter Karmanos generously gave a large donation to the cancer research, patient care and…

On Jan. 1, 1995, Georgia’s Comprehensive Cancer Registry was established. The Registry became gold certified in 2002 following…

In 1995, Information in National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Physician Data Query (PDQ) database became available on the World…

In 1995, The BRCA2 gene was mapped to chromosomal 13q. Just fifteen months later, Wooster et al. reported…

In 1995, the Community Intervention Trial for Smoking Cessation (COMMIT), funded by the Nationa Cancer Institute, was designed…

In 1995, Gene therapy, immune-system modulation and recombinantly produced antibodies enter the clinic in the war against cancer….

In 1995, the FDA declared cigarettes to be “drug delivery devices.” Restrictions were proposed on marketing and sales…
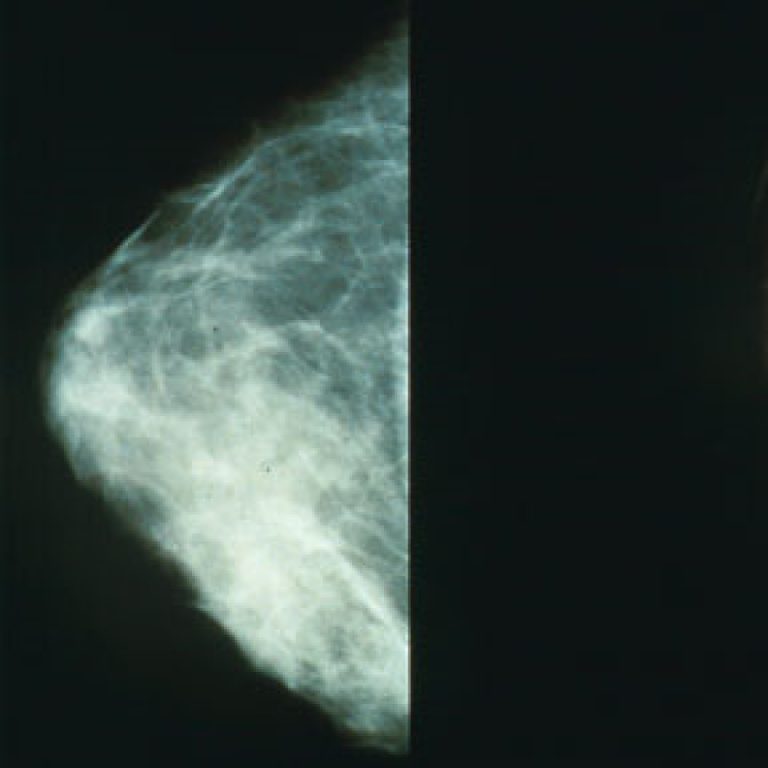
In 1995, scientists cloned the tumor suppressor genes BRCA1 and BRCA2, inherited genetic mutations that can predict an…

In 1995, the Huntsman family led by Jon M. Huntsman Sr. and his wife Karen, pledged $100 million…

In 1995, The Huntsman Cancer Institute, at the University of Utah, is a National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center…

In 1995, Mary-Claire King, an internationally known human geneticist, was recruited to the University of Washington’s (UW) School…

On Oct. 26, 1994, the University of California, Irvine (UCI) Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center (CFCCC) gained designated…

On Oct. 7, 1994, a strong candidate for the 17q-linked BRCA1 gene, which influences susceptibility to breast and…

In Mar. 1994, Penn Medicine’s Dr. Joel Goldwein established OncoLink, the first cancer information site on the Internet,…
On Feb. 25, 1994, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it could consider regulating regulating tobacco…
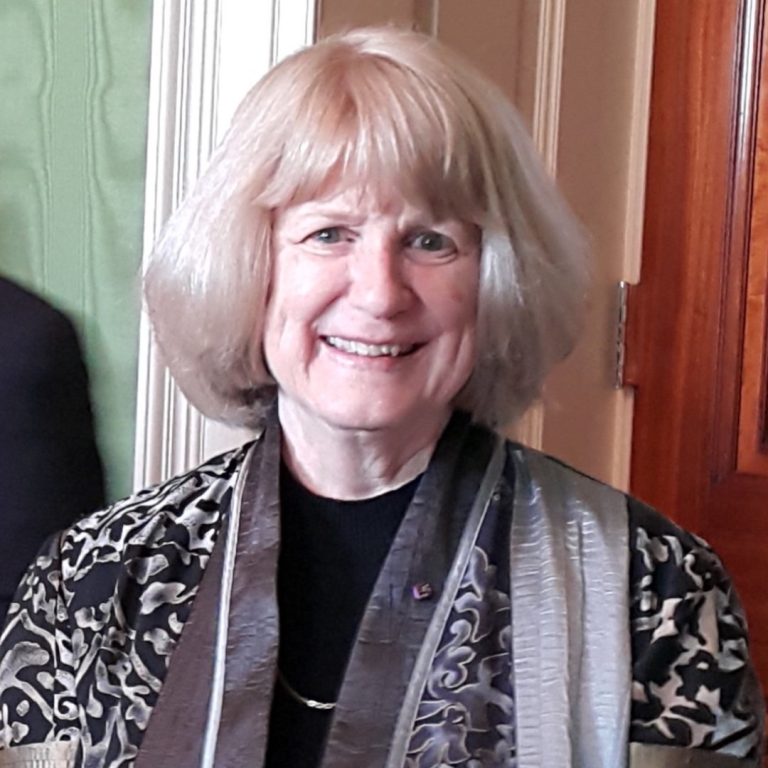

In 1994, Mary-Claire King, PhD, a University of Washington professor of genome sciences and medicine, discovered the “breast…