The Cutter Incident, a production error, caused some polio vaccine to be tainted with live polio virus
In April 1955, Cutter Laboratories, located in Berkeley, California and one of several companies licensed by the U.S….
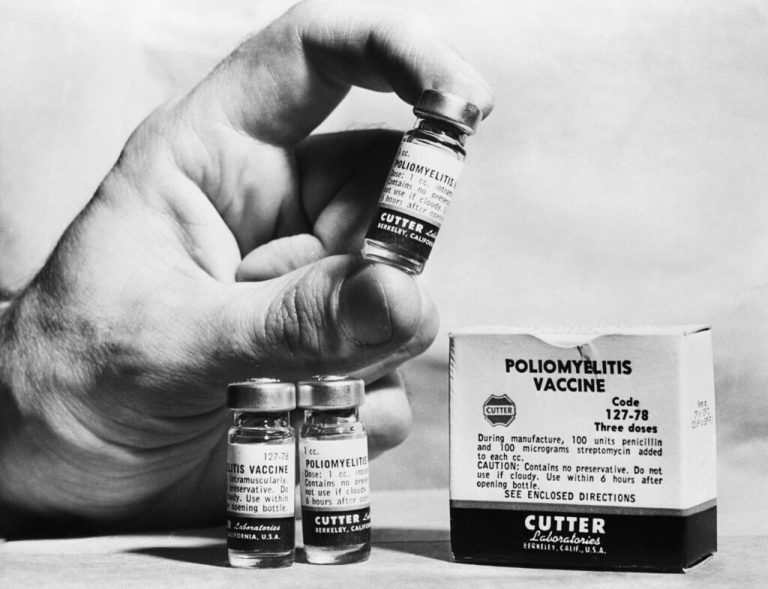
In April 1955, Cutter Laboratories, located in Berkeley, California and one of several companies licensed by the U.S….
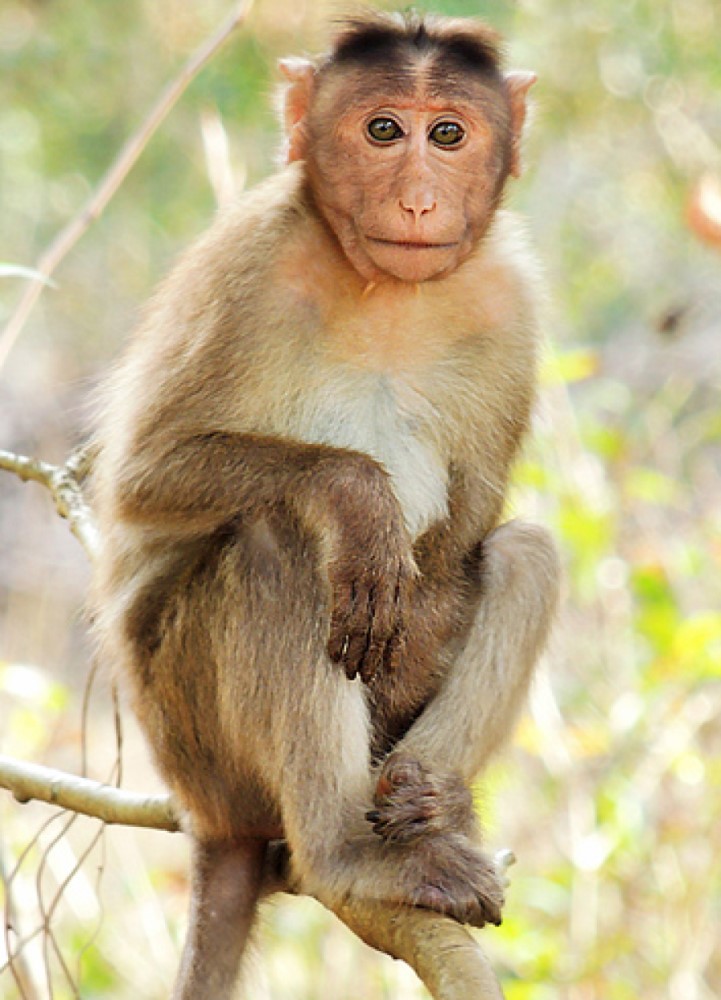

From 1955 through early 1963, millions of people were accidentally exposed to simian virus 40 (SV40) as a…

In 1955, the Division of Biologics Control (DBS) became an independent entity within the National Institutes of Health…
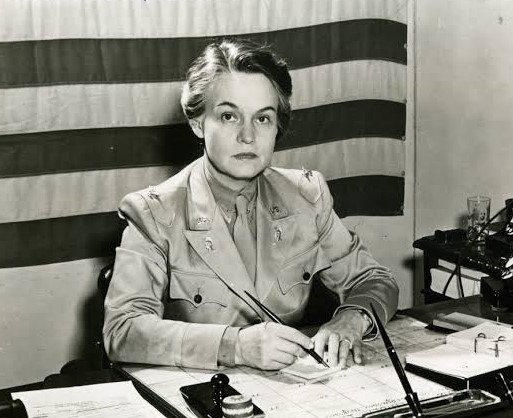

In 1955, Oveta Culp Hobby, the first Secretary of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW) appointed a committee of…

In 1955, the Polio Vaccination Assistance Act was enacted by the U.S. Congress, the first federal involvement in…

In 1955, Canada contributed to the safe cultivation of the poliovirus, using Medium 199, and an incubation process…
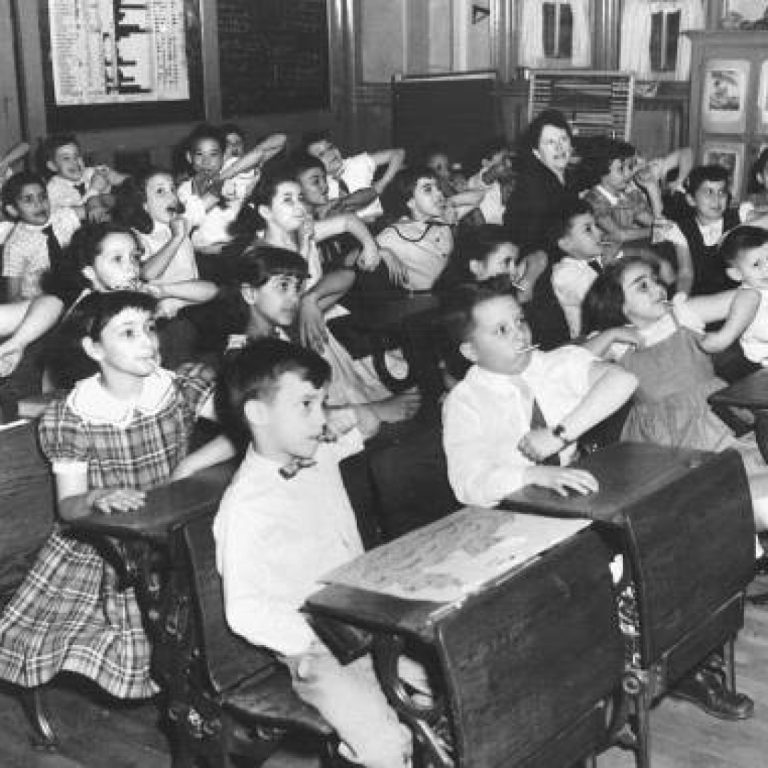

On Apr. 26, 1954, the largest controlled Polio vaccine field trial in the history of medicine got under…

On Apr. 25, 1954, the Vaccine Advisory Committee of the National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis, now known as…

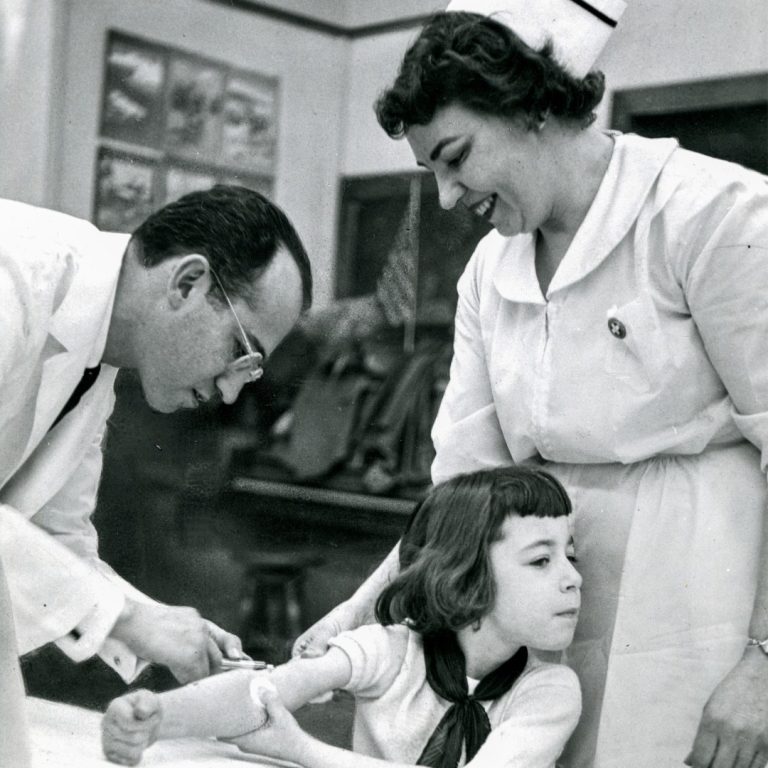
On Feb. 23, 1954, the first mass inoculation of the new Polio vaccine, developed by Dr. Jonas Salk…

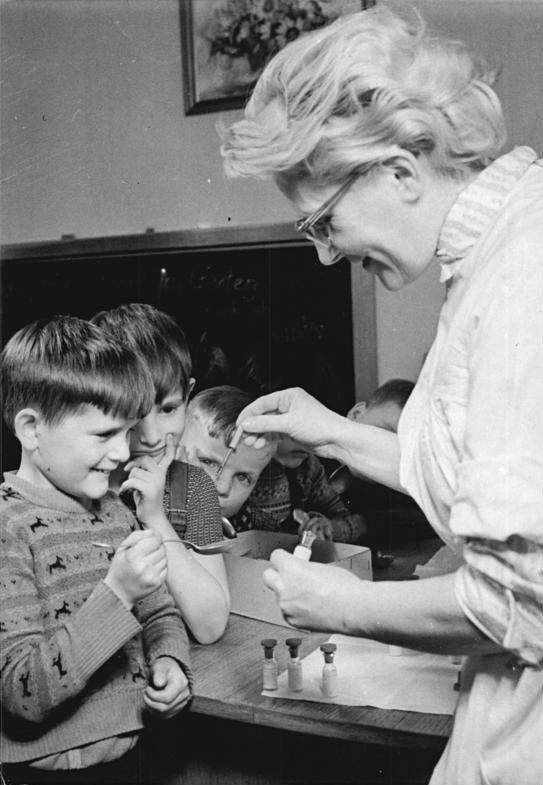
In February 1954, first-, second- and third-grade students from five suburban schools were the first to be inoculated…

In 1954, John Franklin Enders and Thomas C. Peebles isolated measles virus from an 11-year-old boy, David Edmonston….
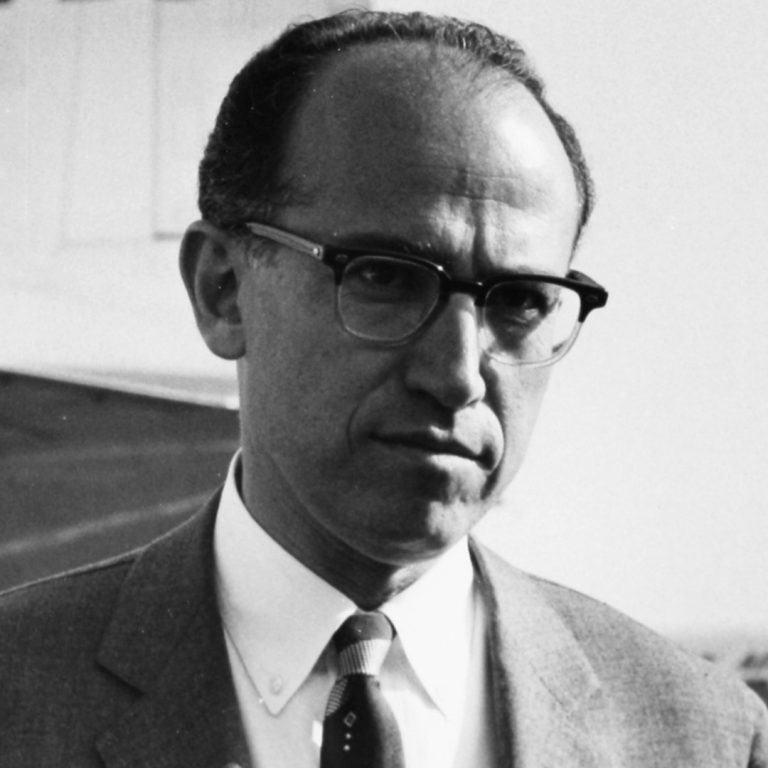

In 1954, Dr. Jonas Salk and associates develop a potentially safe injectable vaccine against polio given to nearly…

On May 16, 1953, Dr. Jonas Salk initiated the first community-based pilot trial of the Polio vaccine in…

On Mar. 28, 1953, Dr. Jonas Salk and his team published a landmark article in the Journal of…
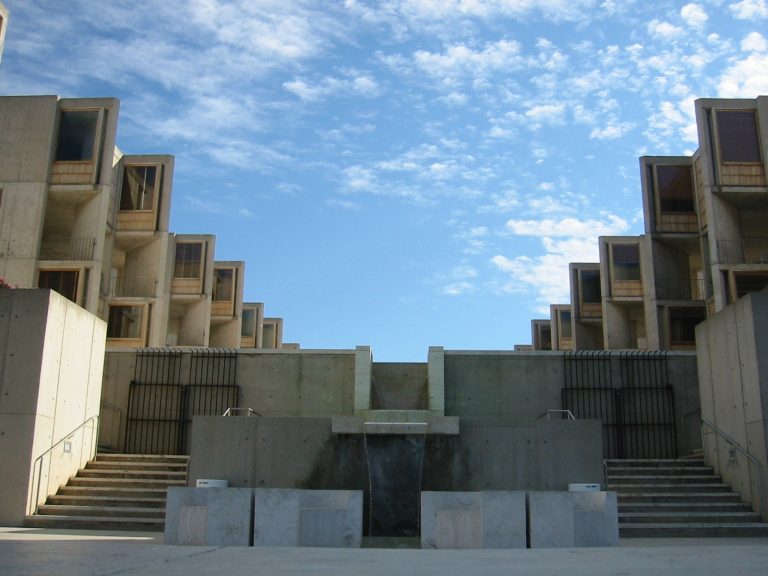

In 1953, the Salk Institute for Biological Studies was founded in La Jolla, California. For more than a…
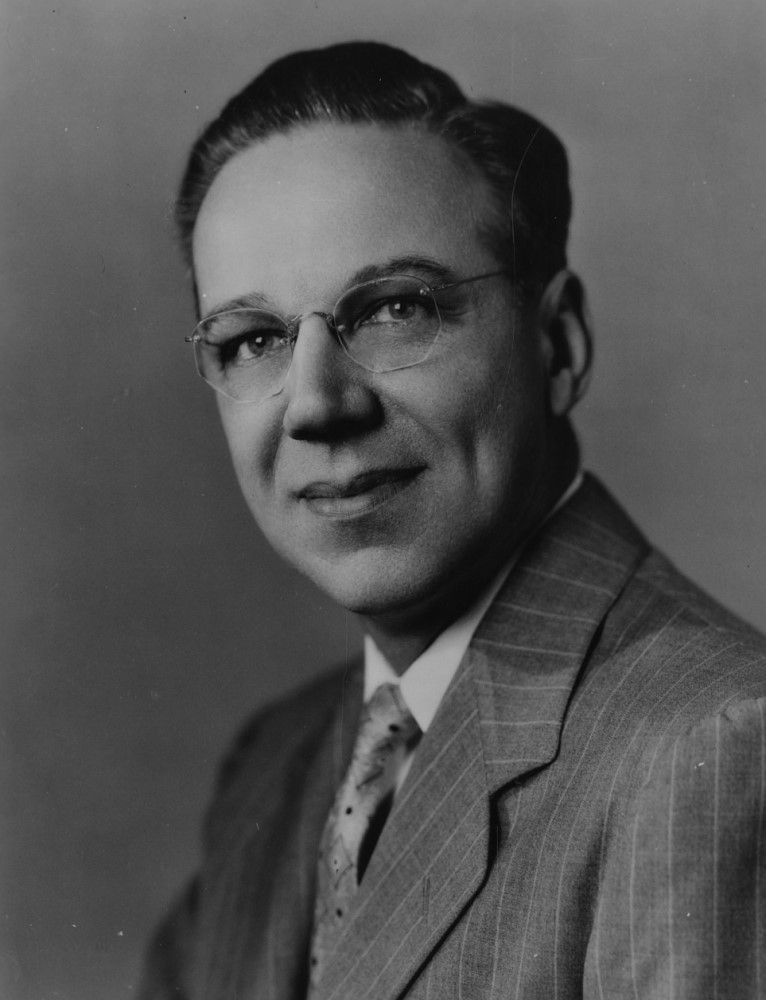

In Oct. 1952, Dr. William McDowall Hammon of the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health published…
On Jun. 12, 1952, Dr. Jonas Salk went to the D. T. Watson Home for Crippled Children (now…
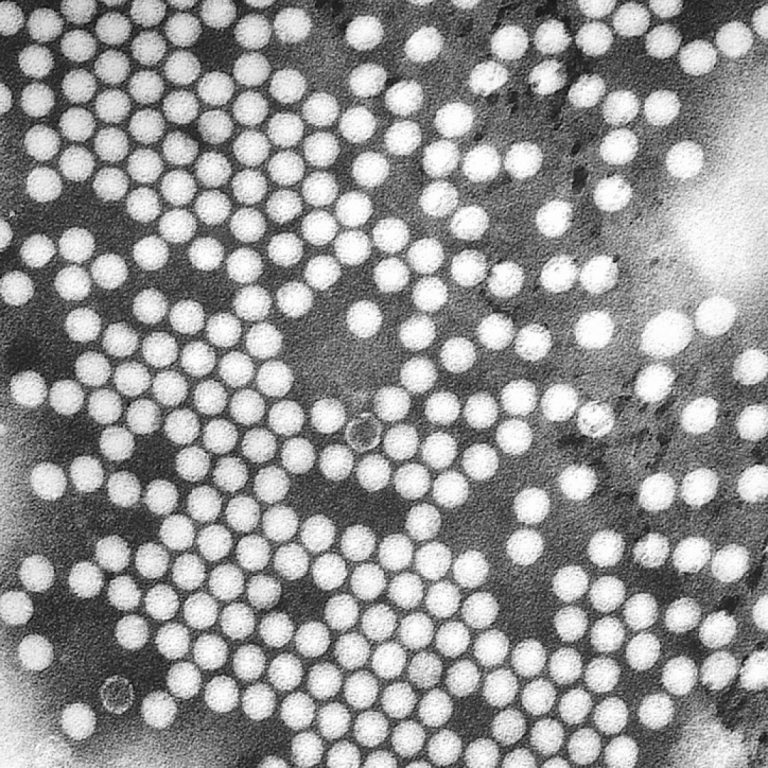
In Jun. and Jul. of 1952, Dr. William Hammon continued with his gamma globulin Polio vaccine field trials…
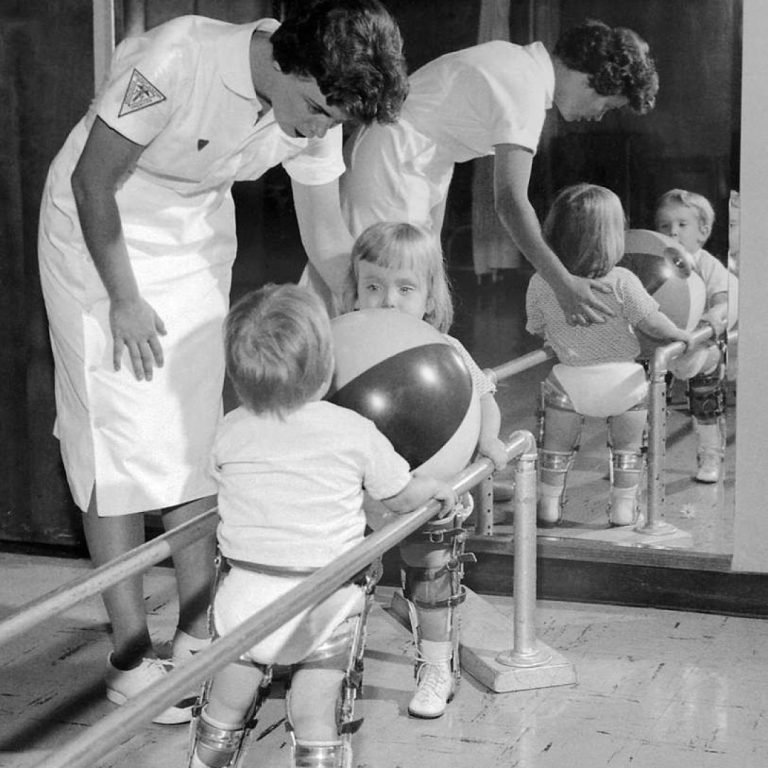

In September 1952, Dr. William Hammon conducted the first placebo-controlled field trial of gamma globulin that, in just…

In 1952, the summer of 1952 recorded 57,628 cases, the worst polio epidemic in U.S. history. This added…
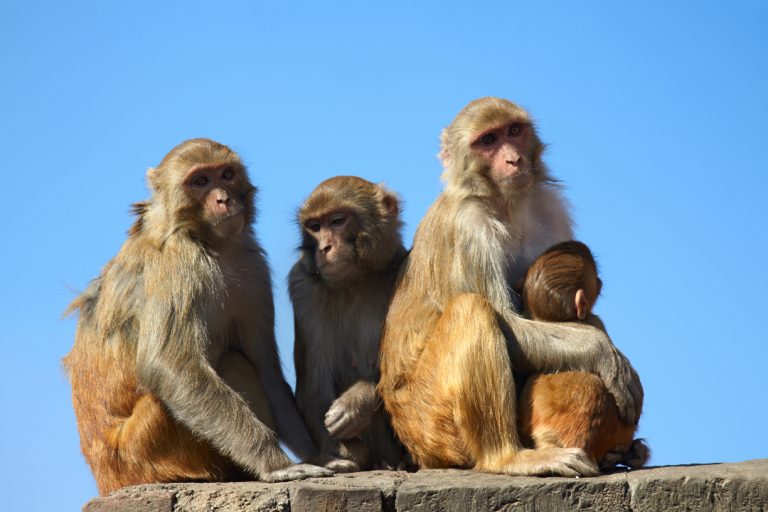

In 1952, Dr. Jonas Salk and his team found monkey kidney tissue to be the most fertile environment…
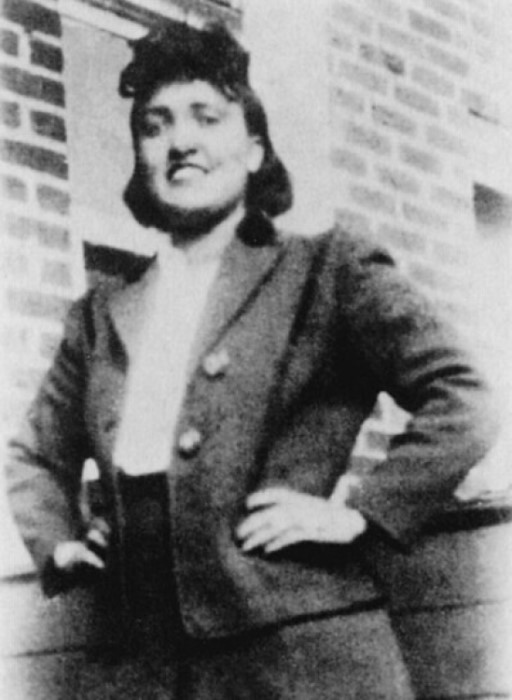

On Feb. 8, 1951, Henrietta Lacks, a tobacco farmer from Virginia died from cervical cancer, and a scientist…

In 1951, Lewis L. Coriell whose history in polio research began during his residency at Children’s Hospital of…
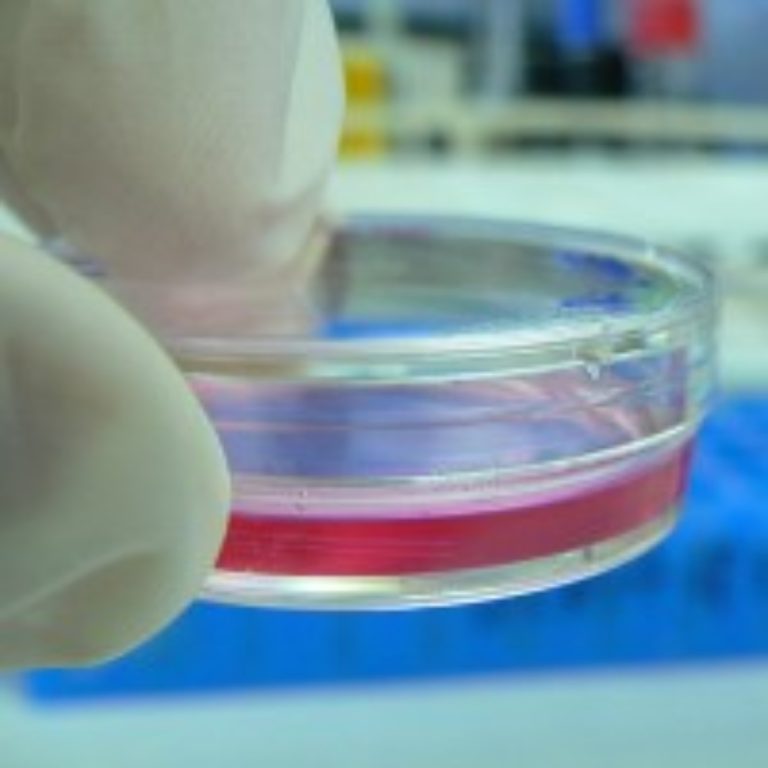
In 1951, Dr. Jonas Salk and his team began using Dr. John F. Enders’ methods to grow poliovirus,…
In 1949, at Harvard, John F. Enders, Ph.D., a Yale College graduate, Frederick C. Robbins, M.D., and Thomas…

In 1949, Dr. Jonas Salk, with grants from the National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis, the Pitt team and…

In 1948, Dr. Isabel M. Morgan led a team that successfully inoculated monkeys with a killed-virurs vaccine. From…

In 1942, Dr. Jonas Salk arrived at the University of Michigan School of Public Health. Techniques earned there…
On Jun. 14, 1940, Charles Armstrong and V. H. Haas published Immunity to the Lansing Strain of Poliomyelitis…
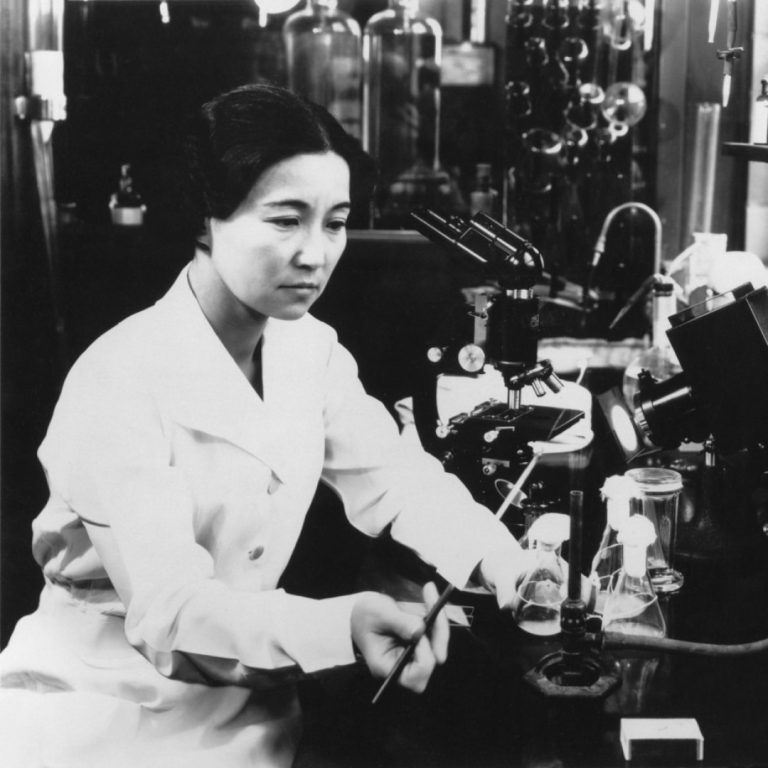

In 1940, biochemist and bacteriologist Ruby Hirose was recognized by the American Chemical Society for accomplishments in chemistry….