The Hollings Cancer Center was founded
In 1993, The Hollings Cancer Center (HCC) was formally was established and named for former U.S. Senator and…
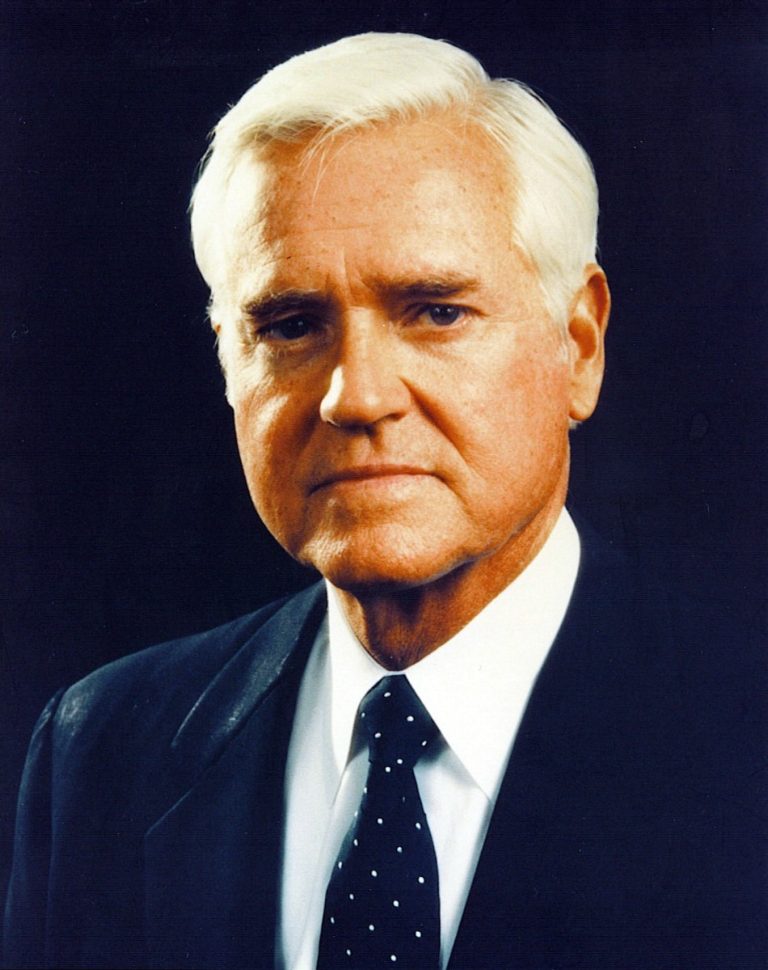

In 1993, The Hollings Cancer Center (HCC) was formally was established and named for former U.S. Senator and…

In 1993, the Vanderbilt Cancer Center was established under the leadership of Dr. Hal Moses, to bring together…

On Oct. 7, 1992, all U.S. mammography facilities, except those managed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, must…

In 1992, the Center for Research on Occupational and Environmental Toxicology (CROET) building opened on the Oregon Health…
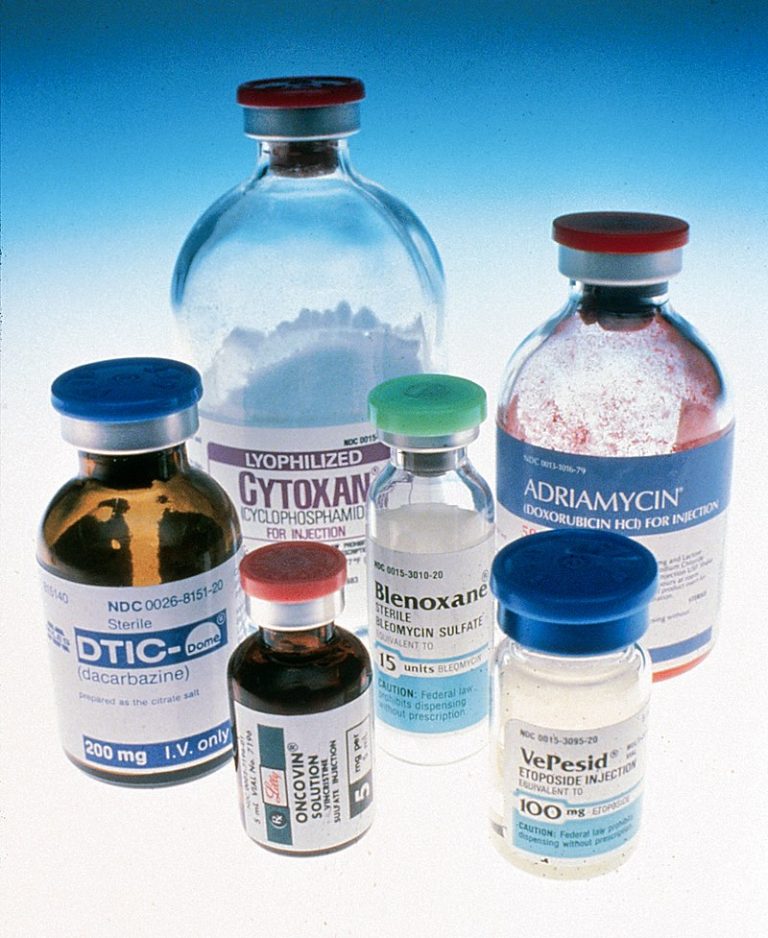
On Mar. 4, 1991, researchers reported that post-operative (adjuvant) radiation therapy and chemotherapy were found to improve survival…
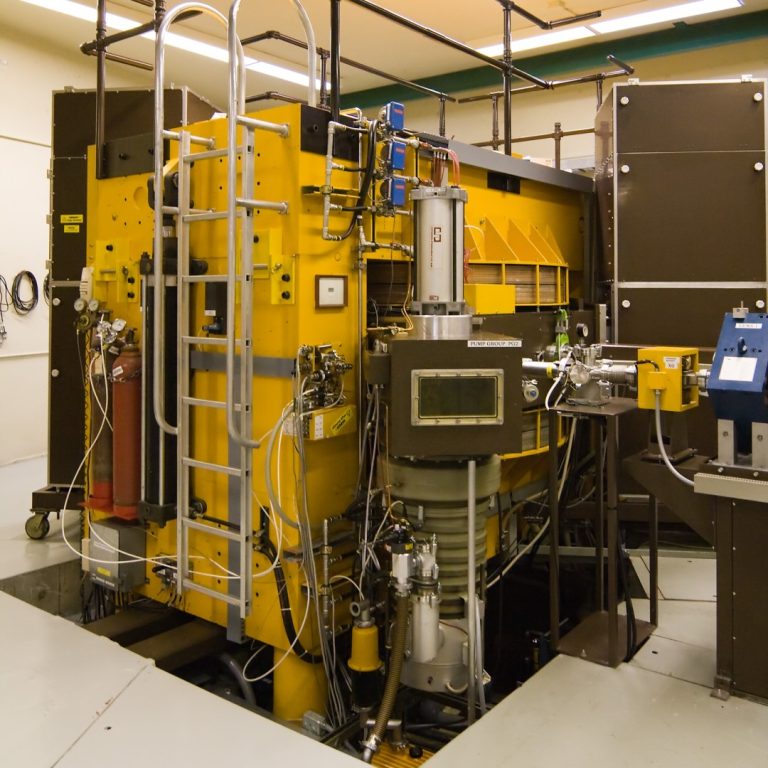

In 1991, the world’s first superconducting cyclotron built to treat cancer was installed at the Gershenson Radiation Oncology…

In 1990, the Dotter Interventional Institute was established at Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) as a multidisciplinary…

In 1989, certification in radiation oncology was first offered. Board certification serves as an important marker for the…
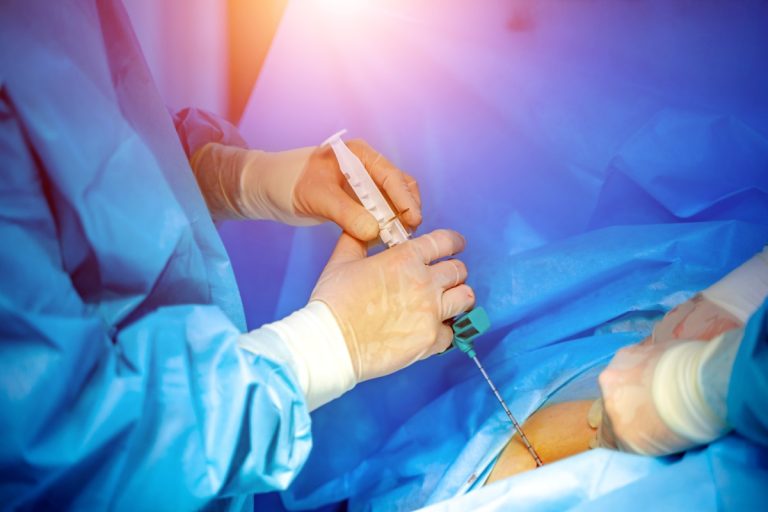
In 1988, oncologists from Yale Cancer Center performed the first bone marrow transplant in Connecticut at the Yale-New…
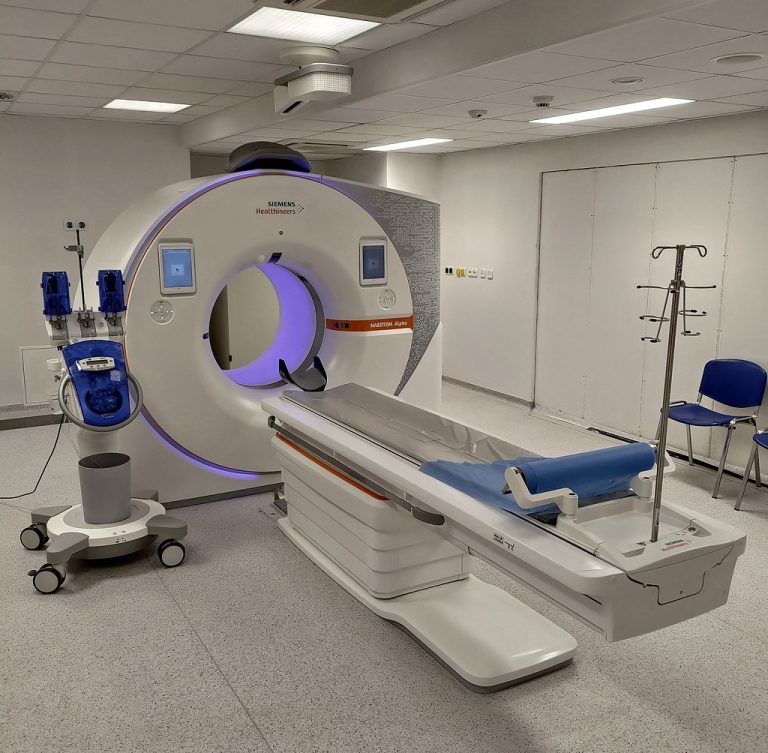
In 1988, radiation oncology physicist James Purdy, PhD and colleagues at Washington University School of Medicine developed a…

In 1987, The National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Cancer Prevention Fellowship Program, one of the first formal postdoctoral research…

In 1987, the University of Minnesota Cancer Center, now known as the Masonic Cancer Center, received National Cancer…
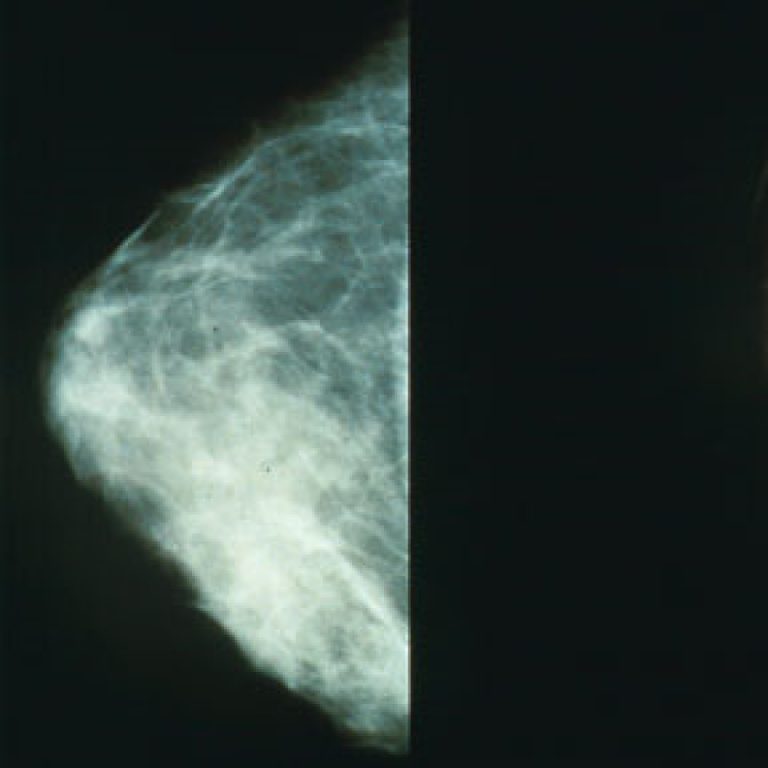
In 1986, the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology and the former Barnes Hospital introduced the first mobile mammography unit…
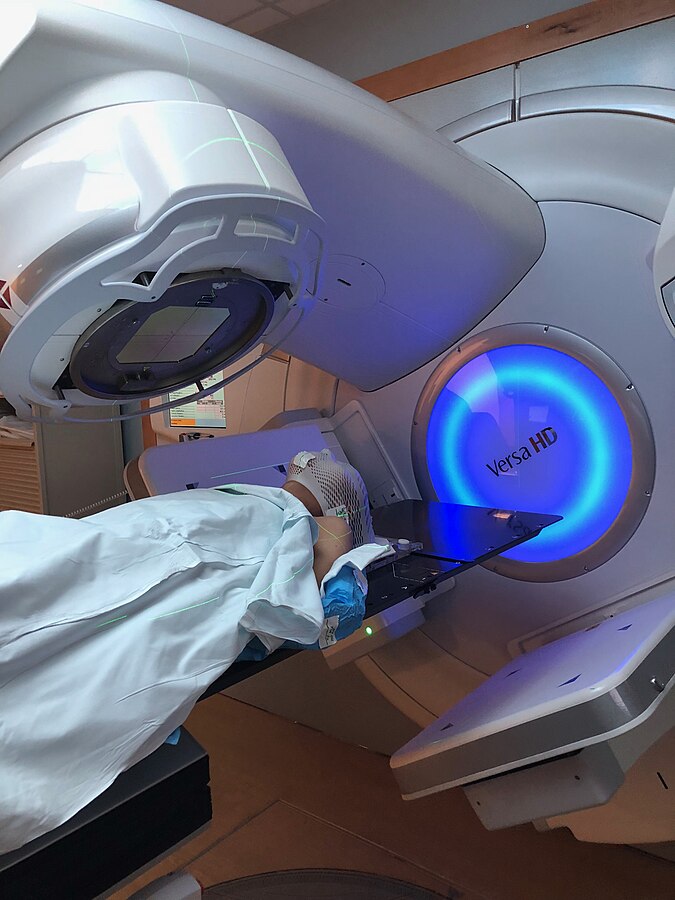
In 1985, Lumpectomy plus radiation therapy was found equivalent to mastectomy for early breast cancer. Lumpectomy followed by…

On May 2, 1984, the new UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Centerメs original three-story cancer research building opened. In…

In 1984, American Cancer Society (ACS) introduced dietary guidelines to reduce cancer. The ACS published Nutrition and Physical…

In 1984, The Comprehensive Minority Biomedical Program, DEA, was established to widen the focus of the minority effort…
In 1984, fluoroestradiol (FES) was first developed by researchers Michael J. Welch, PhD from Washington University at St….

On Jul. 16, 1983, the National Cancer Institute launched the Community Clinical Oncology Program (CCOP) to provide a…

On Feb. 3, 1983, the University of Southern California Kenneth Norris Jr. Cancer Hospital and Research Institute (USC…

In 1983, The Meyer L. Prentis Comprehensive Cancer Center of Metropolitan Detroit now known as the Karmanos Cancer…

In 1983, the National Cancer Institute formed the Division of Cancer Prevention and Control to accelerate the science…

In 1982, the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Physician Data Query (PDQ) cancer information database went online. PDQ is…

In 1982, the Fred Hutch established the Cancer Prevention Program in Seattle, which has made key contributions to…

In 1981, John Wayne Cancer Institute (formerly known as the John Wayne Cancer Clinic) was founded to promote…

In 1981, The University of Hawaii Cancer Center (UH Cancer Center) was founded. The UH Cancer Center’s mission…
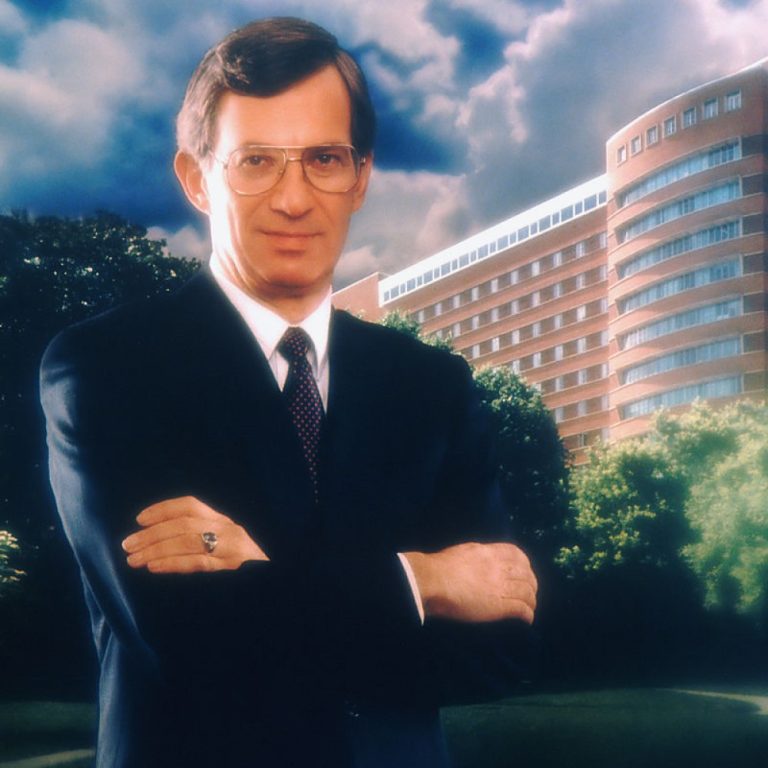

On Jul. 9, 1980, Dr. Vincent T. DeVita, Jr. became the ninth director of the National Cancer Institute…
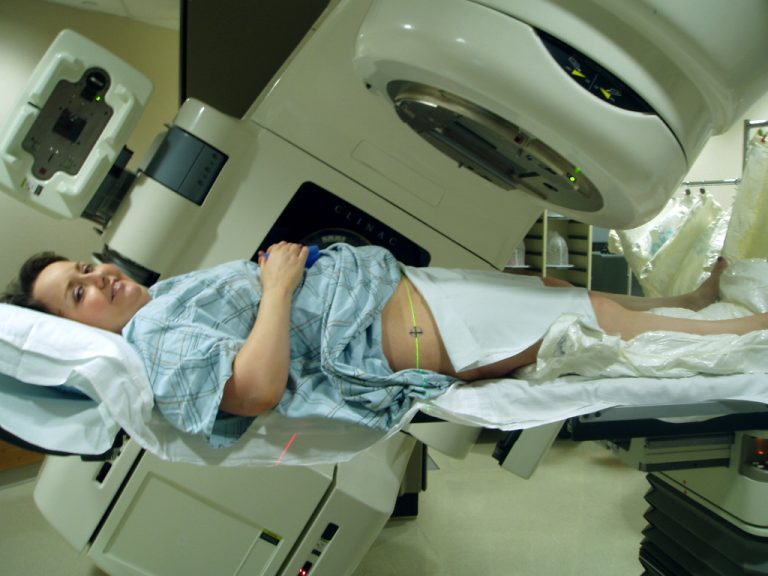
In 1980, the $2 million Gershenson Radiation Oncology Center (GROC) opened as a partnership between Wayne State University’s…

On Dec. 27, 1979, the U.S. Congress approved the change of the Laboratory’s name to Lawrence Livermore National…

On Dec. 6, 1979, public Law 96-164 [S. 673] passed by the U.S. Congress, was signed by President…