The Albert Einstein Cancer Center (AECC) was established
In 1971, The Albert E instein Cancer Center (AECC) was established. The goals of AECC are to foster…

In 1971, The Albert E instein Cancer Center (AECC) was established. The goals of AECC are to foster…

In 1971, The Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research was established by American businessman Daniel K. Ludwig to support…

In 1971, The MD Anderson Cancer Center became one of the nation’s first NCI-designated comprehensive cancer centers. Today,…

On Oct. 18, 1970, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation was founded. The MacArthur’s business interests…
In 1970, Cisplatin, a platinum-containing anticancer compound with unique biologic effects, entered clinical trials. On Dec. 19, 1978,…
In 1970, flexible sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy were introduced to locate and remove precancerous growths in the colon. Clinical…

In 1970, The Cancer Center at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies was established. Research at the Center…

In 1970, Senator Norris Cotton secured a $3 million federal grant to build rural New England’s first regional…
In 1969, Robert Huebner and George Todaro proposed the oncogene hypothesis. An oncogene is a gene that has…
In 1969, the Michigan Cancer Foundation’s cancer registry began recording every incidence of cancer in southeastern Michigan. It…

In 1968, the world’s first successful bone-marrow transplant was completed at the University of Minnesota Hospital under the…

On Feb. 13, 1967, a cancer research center, USPHS Hospital, was established in Baltimore by the institute to…

In 1967, the guaiac fecal occult blood test (FOBT) was introduced as a screening test for colorectal cancer….

In 1967, the construction of the Salk Institute for Biological Studies was completed. the original Institute buildings were…

In 1967, E.R. Squibb & Sons delved into cancer research, discovering and developing hydroxyurea for leukemia and advanced…

In 1966, the NCI standardized the testing of cancer-causing chemicals. The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)

In 1965, McGill University researchers Dr. Phil Gold and Dr. Samuel O. Freedman co-discovered the first identifiable cancer…

In 1965, The Hutch Award’s was created in honor of the late Fred Hutchinson, the courageous and inspirational…

On Dec. 9. 1964, President Johnson received the report of the President’s Commission on Heart Disease, Cancer and…
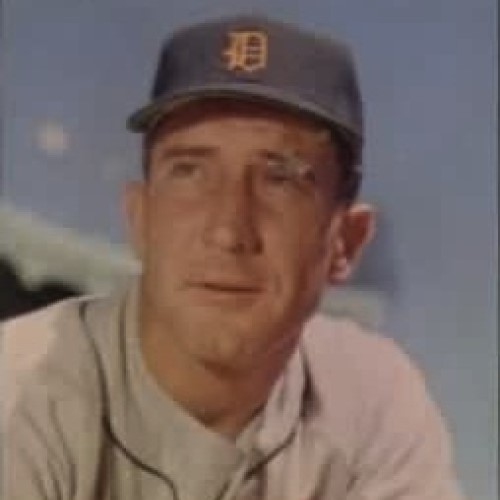

On Nov. 12, 1964, Fred Hutchinson, a standout pitcher at Seattle’s Franklin High School and ten year pitching…

On Jan. 11, 1964 U.S. Surgeon General Luther Terry released the first government report that concluded smoking may…

In 1964, the anticancer drug melphalan (L-PAM) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
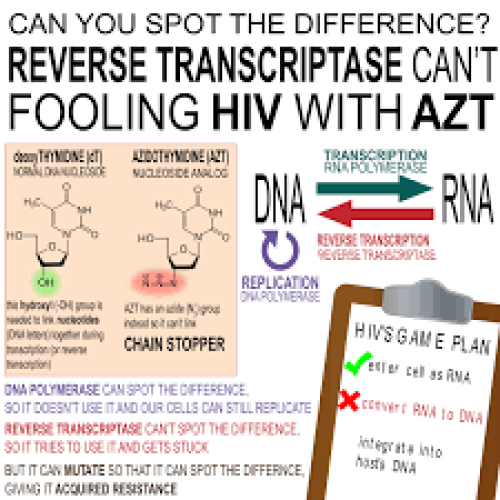
In 1964, the anticancer drug Azidothymidine (AZT) was synthesized in Michigan Cancer Foundation’s chemistry lab by Jerome Horwitz,…

In 1963, Yale New Haven Hospital (then Grace-New Haven) installed the first linear accelerator in Connecticut for cancer…

In 1963, the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology at Washington University – St. Louis installed the Picker Cobalt 60,…

On May 7, 1962, the Acute Leukemia Task Force held its first meeting. It focused the combined efforts…
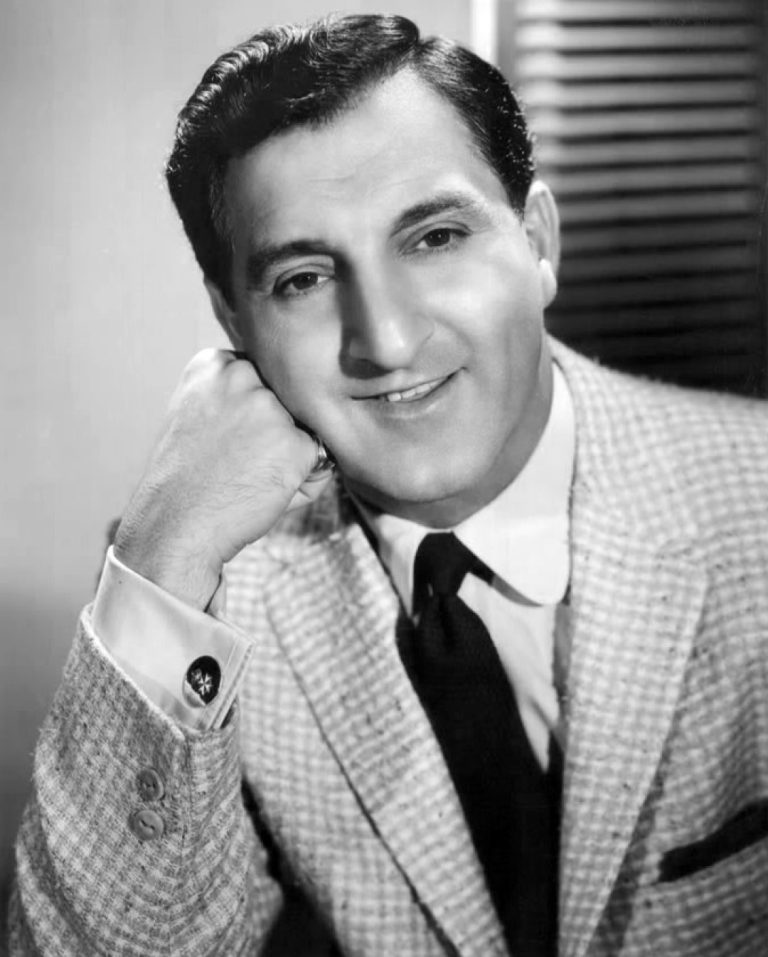

On Feb. 4, 1962, St.ᅠ Jude Children’s Research Hospital opened it’s doors.This was the day that Danny Thomas…

in 1962, Iowa Methodist Medical Center established Iowa’s first hospital-based radiation oncology department and remains a leader in…

In 1962, the Royal College of Physicians issued a report on smoking and health.
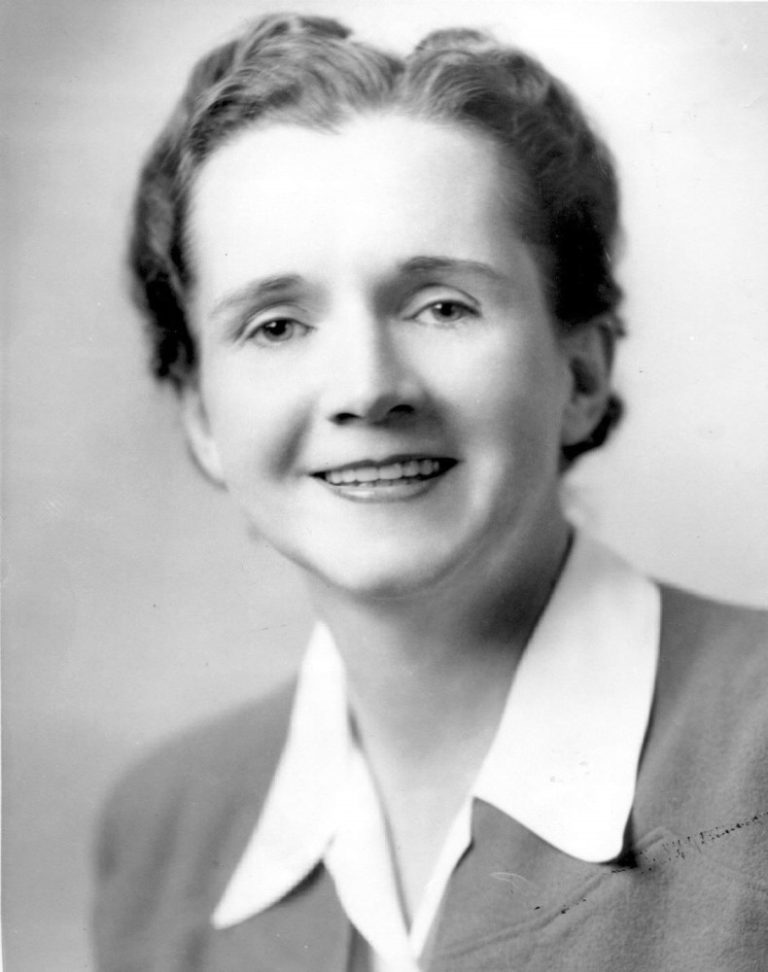

In 1962, Silent Spring, a book by marine biologist Rachel Carson, galvanized the first generation of environmentalists. Silent…