President Kennedy swore in Luther Terry as US Surgeon General
On Mar. 2, 1961, President Kennedy swore in Luther Leonidas Terry as U.S. Surgeon General. The landmark Surgeon…

On Mar. 2, 1961, President Kennedy swore in Luther Leonidas Terry as U.S. Surgeon General. The landmark Surgeon…
In 1961, platelet concentrates were recognized for reducing the mortality from hemorrhage in cancer patients.

In 1961, the CDC expanded its reach into chronic disease by investigating a cancer cluster in Illinois.

On Sept. 21, 1960, FDA officials announced the last remaining major source of the discredited Hoxsey cancer treatment…

In 1960, The Eppley Cancer Center, now a National Cancer Institute Laboratory Cancer Research Center, began in the…

In 1960, the construction of the first McArdle building resulted from a gift by Michael W. McArdle. Dr….

On Nov. 16, 1959, Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), an alkylating agent designed to improve the selectivity of cancer drugs, was…

In 1959, the Journal of the National Cancer Institute inaugurated a series of occasional publications as Monographs to…

In 1959, University of Western Ontario researchers Dr. Charles Beer and Dr. Robert L. Noble developed the anti-cancer…
In 1957, Charles Heidelberger introduces 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a new type of anticancer drug that resulted from rational design.
In 1957, Roy Hertz and Min Chiu Li achieve the first completed cure of a human solid tumor…

In 1956, Stanford Medicine became the first to use linear accelerator to treat cancer in Western hemisphere.

On Apr. 1, 1955, the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Chemotherapy National Service Center was established in the institute…

In 1955, The National Cancer Chemotherapy Program was initiated. It was administered and integrated by the Division of…

In 1955, the NCIメs Cooperative Group Program for clinical research was established in 1955 and has grown to…
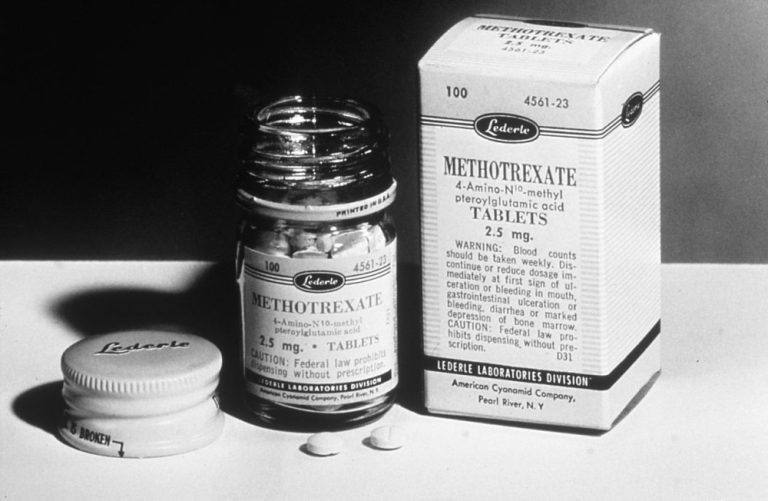
On Dec. 7, 1953, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved methotrexate, an antimetabolite derived from folic…

On Jan. 27, 1953, the Cancer Research Institute was founded by Helen Coley Nauts, and is the worldメs…
In 1953, Yale established the first pharmacology department in the U.S. to focus on cancer chemotherapy and cancer…

In 1952, Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase conducted a series of experiments at the Carnegie Institute of Washington…

On Jun. 1, 1951, the Ben May Laboratory for Cancer Research at the University of Chicago opened its…
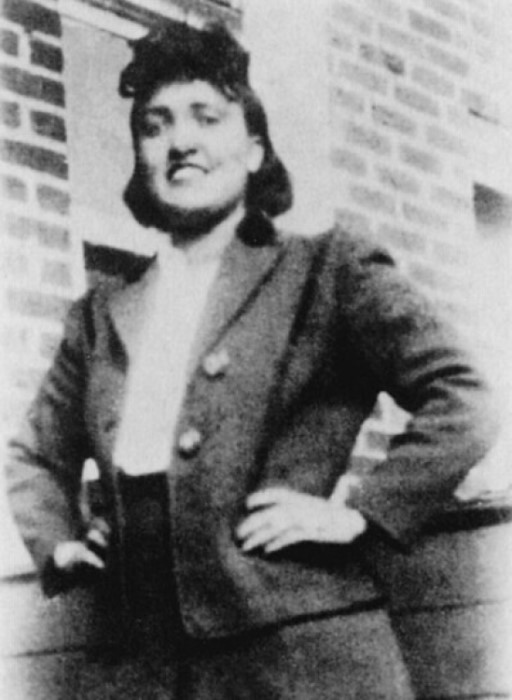

On Feb. 8, 1951, Henrietta Lacks, a tobacco farmer from Virginia died from cervical cancer, and a scientist…
In 1950, Ernst Wynder, Evarts Graham, and Sir Richard Doll confirmed the cigarette smoking-cancer link. In 1950, Wynder…

In 1950, the Delaney Committee started congressional investigation of the safety of chemicals in foods and cosmetics, laying…

In 1950, Sidney Farber and colleagues achieved the first remissions in Wilms tumor of the kidney, a common…
In 1950, the Michigan Cancer Foundation and the American Cancer Society began sponsoring new cancer research and outreach…

In 1949, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved nitrogen mustard to kill cancer cells. The major use…

In 1949, Canadaメs first full-time cancer physicist, Dr. Harold Johns, led the world in development the cobalt bomb…

In 1948, the National Cancer Institute’s grants program to medical, dental, and osteopathic schools was initiated for improvement…

In 1947, The first attempt at coordinating cancer at University of California at San Francisco (UCSF) was a…

In 1948, the Detroit Cancer Center was established from the union of the Detroit Institute for Cancer Research…