Dr. David Hume, a pioneer transplant surgeon, was appointed chairman and professor of surgery at the Medical College of Virginia
In 1956, Dr. David Hume, a pioneer transplant surgeon, was appointed chairman and professor of surgery at The…
In 1956, Dr. David Hume, a pioneer transplant surgeon, was appointed chairman and professor of surgery at The…
In 1953, William P. Murphy, Jr., an American doctor working with colleague Carl Walter, developed the blood bag…
In 1952, Felix Bloch at Stanford University and Edward Mills Purcell at Harvard University were awarded the Nobel…
In 1950, Schepens Eye Research Institute of Massachusetts Eye and Ear was founded to fight blindness by developing…

In 1949, the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to Arthur B. Lamb ‘for his numerous contributions…
In 1949, at Harvard, John F. Enders, Ph.D., a Yale College graduate, Frederick C. Robbins, M.D., and Thomas…

In 1947, the Priestley Medal was awarded to Warren K. Lewis by the American Chemical Society “to recognize…

In 1946, the Priestley Medal was awarded to Roger Adams by the American Chemical Society “to recognize distinguished…

In 1944, the the American Chemical Society awarded the Priestley Medal to James B. Conant “to recognize distinguished…
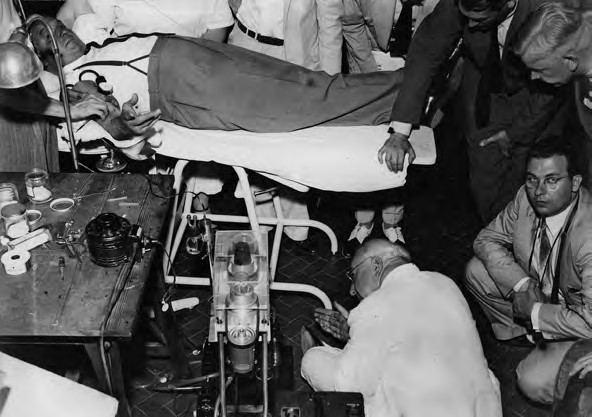
In 1940, Edwin Cohn, a professor of biological chemistry at Harvard Medical School, developed cold ethanol fractionation, the…

In 1934, William Perry Murphy, who shared the Nobel Prize for Medicine for discoveries concerning liver therapy in…

On Oct. 12, 1928, the first iron lung was used at Boston Children’s Hospital by Harvard Medical School…
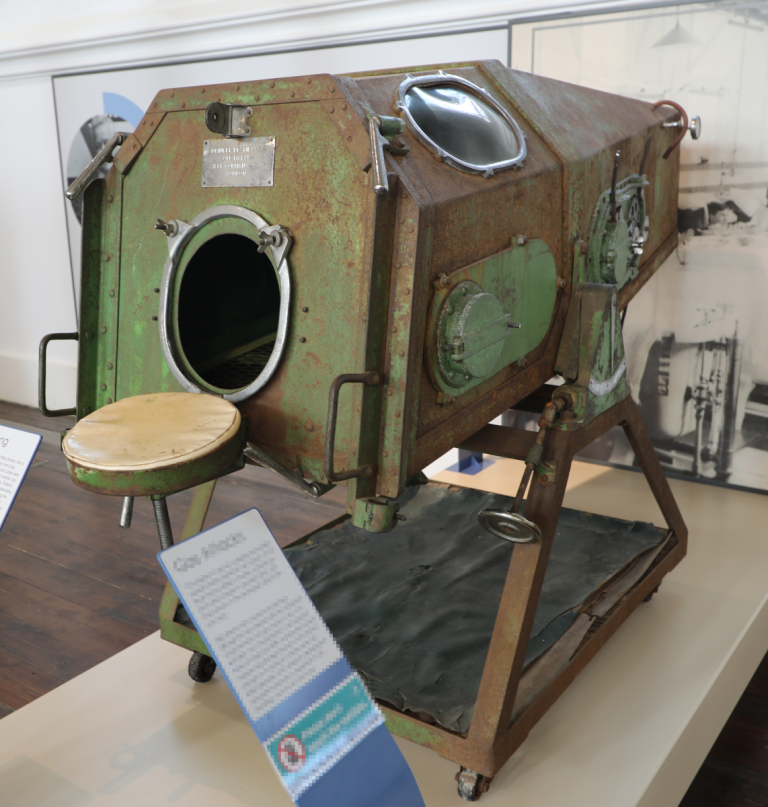

In 1927, the iron lung was developed by Philip Drinker and Louis Agassiz Shaw at Harvard School of…

In 1925, Joseph W. Schereschewsky, head of a PHS Special Cancer Investigations Laboratory established in 1922 in Cambridge,…

In 1922, the Public Health Service opened a Special Cancer Investigations Laboratory at Harvard Medical School.

In 1922, Elliott Joslin, at Harvard Medical Center, introduced insulin to the United States and founded Joslin Diabetes…
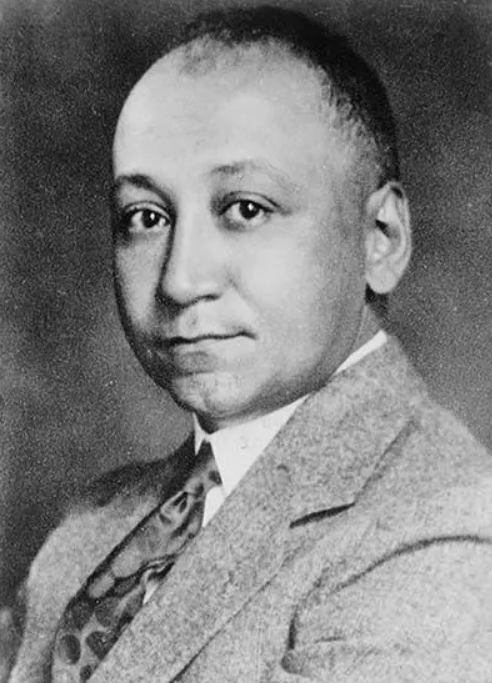

In 1919, Dr. Louis T. Wright became the first African American physician at Harlem Hospital. Wright earned a…
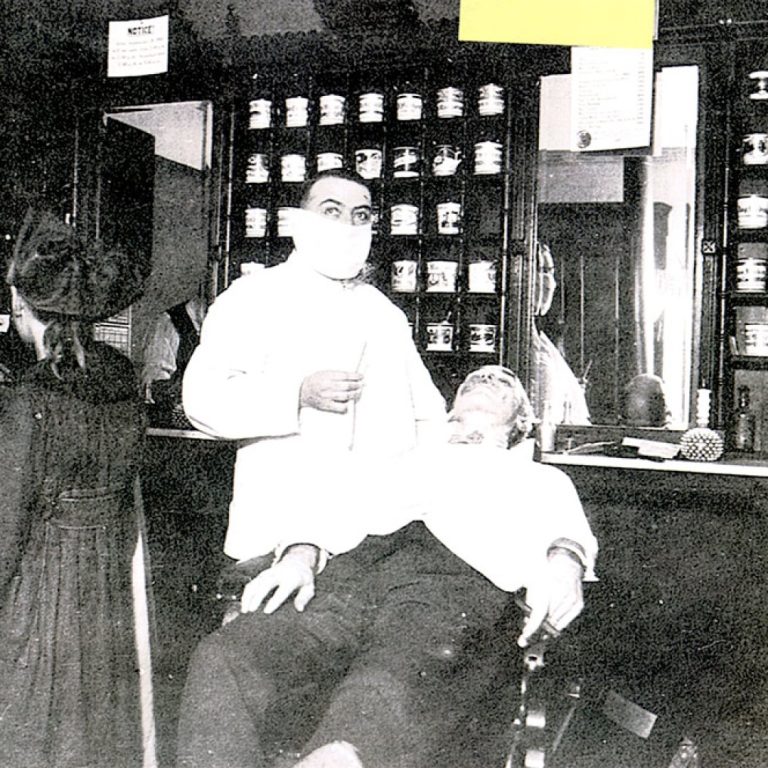

On Oct. 19, 1918, Boston’s influenza closure ordered were removed, allowing public spaces to reopen.
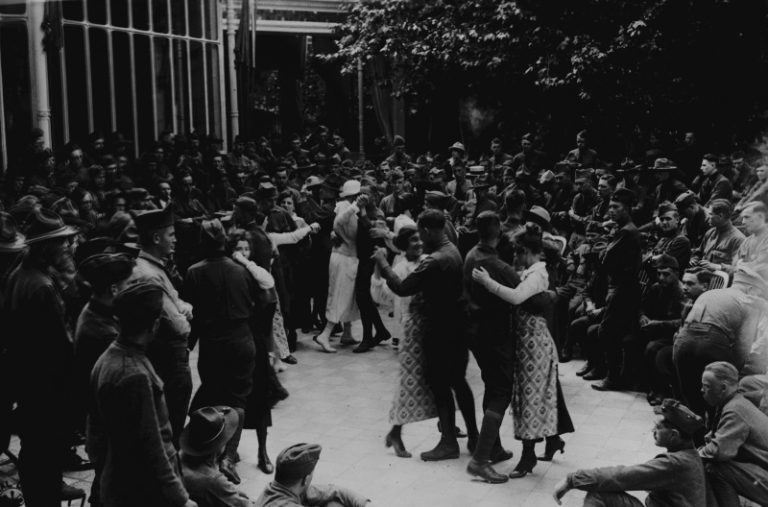

By Oct. 15, 1918, over 3,500 Bostonians had died from influenza or resulting pneumonia since the epidemic began….

On Oct. 8, 1918, Boston’s health commissioner Dr. William C. Woodward ordered reduced hours for various stores in…
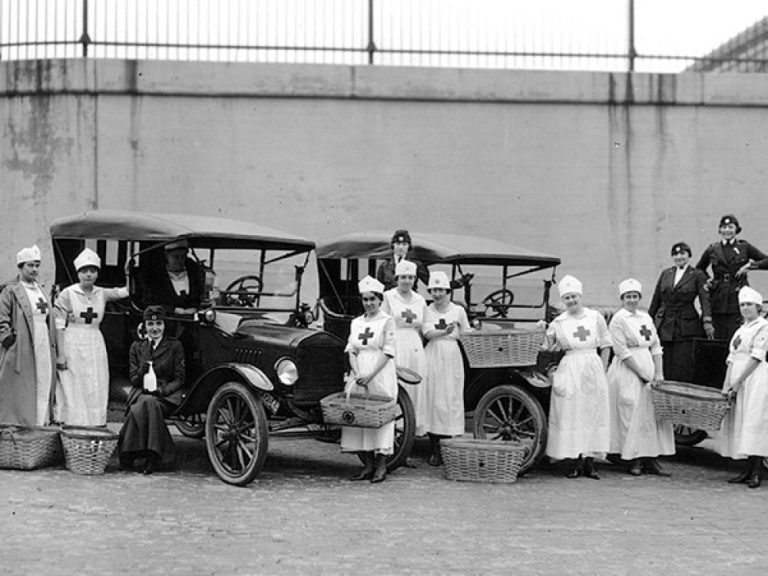

On Oct. 2, 1918, the Massachusetts Department of Health made influenza a reportable disease.

On Sep. 26, 1918, Boston’s health commissioner Dr. William C. Woodward issued a closure order for theaters, movie…

On Sept. 25, 1918, Boston’s health commissioner Dr. William C. Woodward announced that all Boston public schools were…

On Sept. 25, 1918, Boston Mayor Andrew J. Peters appointed an Emergency Committee to advise and empower the…
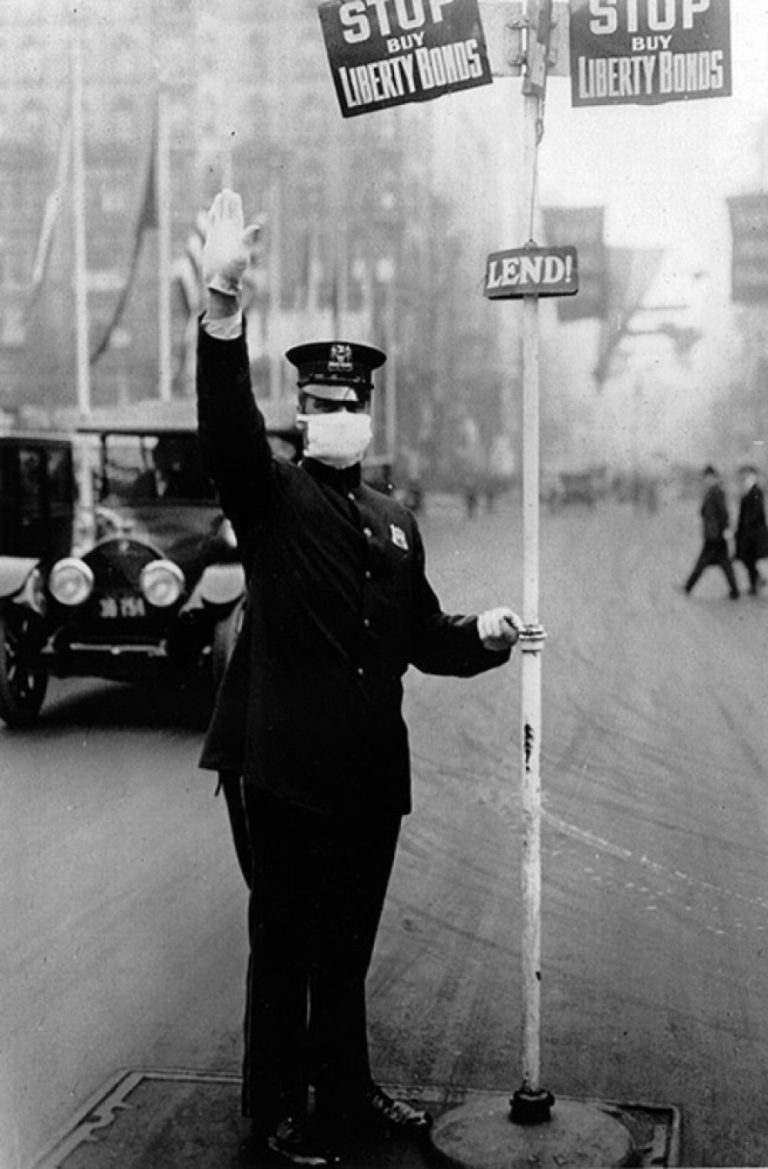

On Sept. 24, 1918, Massachusetts Governor Samuel W. McCall held a conference call with state health and safety…
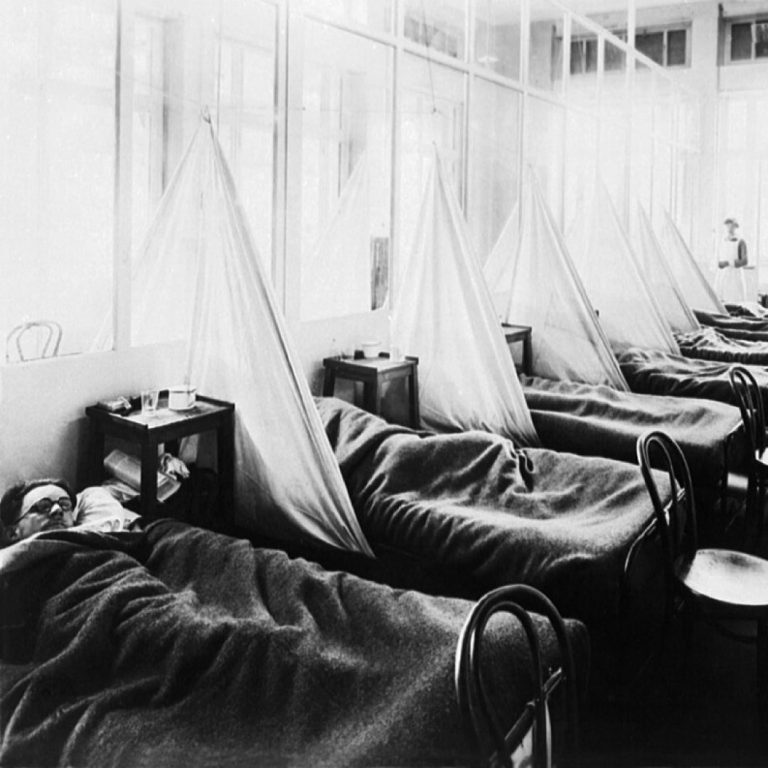
By Sept. 23, 1918, the total number of influenza victims jumped to 334. That situation was growing increasingly…
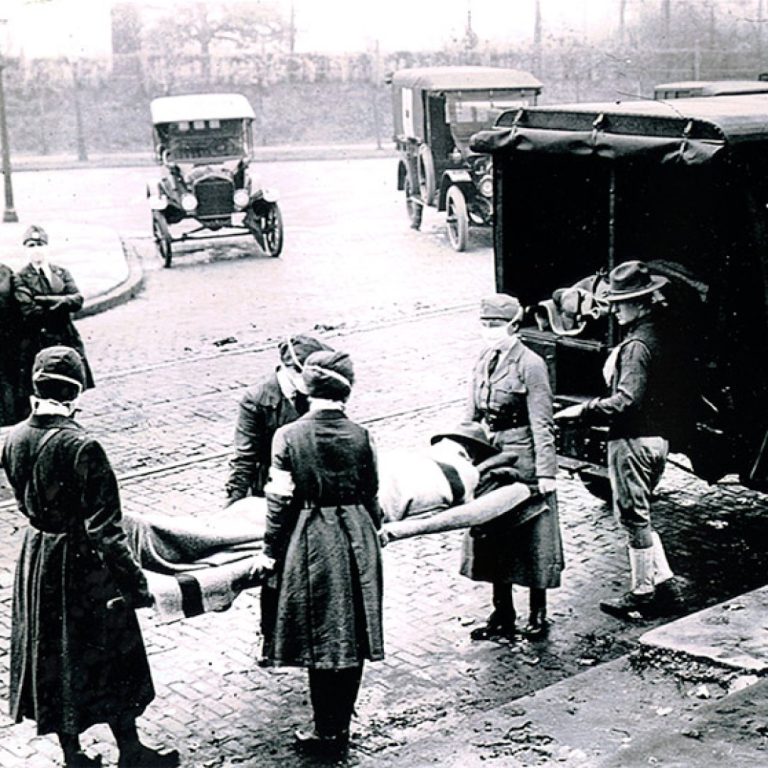

By Sept. 16, 1918, hundreds of influenza cases existed in the city of Boston, overcrowding hospitals.
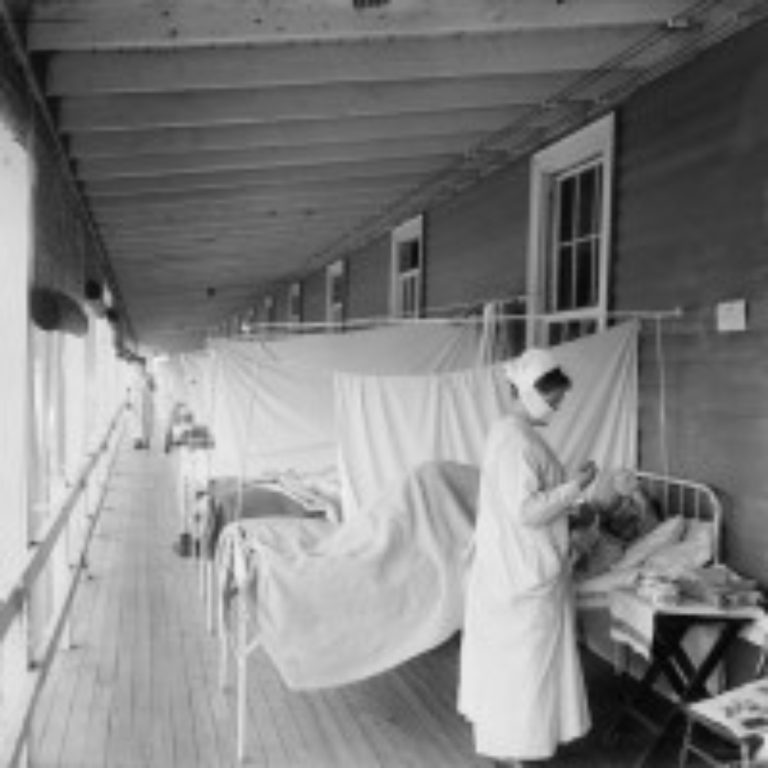
On Sept. 11, 1918, the first civilian influenza cases were reported in Boston. By Sept. 16, there were…
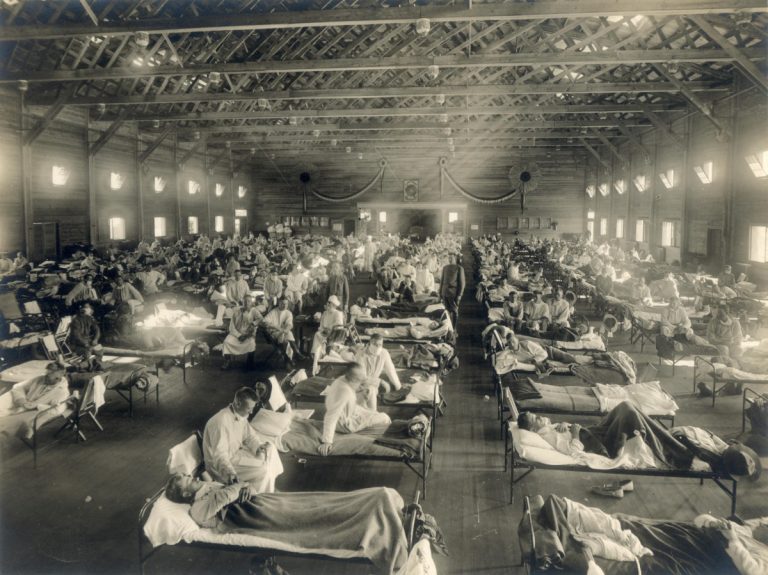
On Sept. 10, 1918, two hundred sick sailors were admitted to the new emergency hospital. Meanwhile, Chelsea Naval…
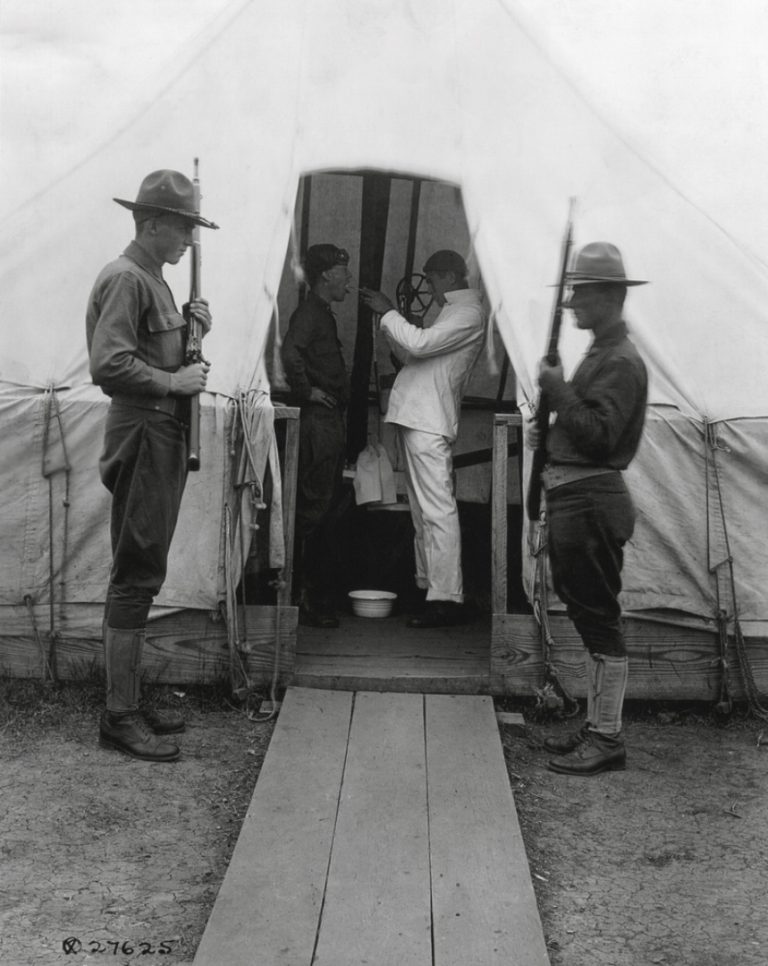

On Sept. 9, 1918, the Massachusetts National Guard, under the direction of Colonel William H. Brooks, erected a…