The Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center was established
On Jun. 9, 1999, the Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center (VRC) was established at the National…

On Jun. 9, 1999, the Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center (VRC) was established at the National…

In April 1999, a pandemic planning framework was published by the World Health Organization (WHO) that emphasized the…
On Jan. 15. 1999, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices…
In 1999, a meningococcal group C conjugate vaccine was introduced into the routine schedule in the U.K. for…

In 1999, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) launched the National Pharmaceutical Stockpile, now the…

In 1999, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) established the Laboratory Response Network (LRN). The…
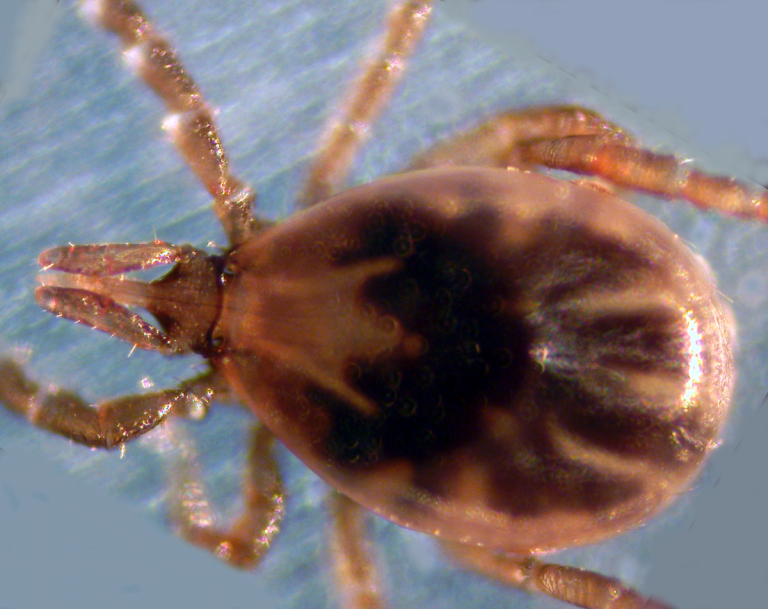

On Dec. 21, 1998, the Lyme Disease Vaccine (Recombinant OspA), (LYMErix by SmithKline Beecham) was licensed for use…

On Aug. 31, 1998, Rotashield (Wyeth Laboratories, Marietta, Pennsylvania) was licensed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration…
On Aug. 26, 1998, Bill and Melinda Gates announced the establishment of the Bill and Melinda Gates Children’s Vaccine…
On Jul. 29, 1998, the diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine adsorbed (Certiva by North American…

In March 1998, the Stop TB Initiative was established following a meeting of the First Ad hoc Committee…
In 1998, some research caused concern that hepatitis B vaccination might be linked with multiple sclerosis (MS), a…
On Oct. 20, 1997, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed Purified Chick Embryo Cell (PCEC, RabAvert®) vaccine…
On April 4, 1997, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) recommended that the vaccine be used more extensively…

On Feb. 13, 1997, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) Annual Meeting and Science Innovation…

In 1997, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP) recommended adoption of a sequential series of two doses of…

In 1997, FluNet, a global web-based tool for influenza virological surveillance was launched. It is a critical tool…

In 1997, the H5N1 bird flu incident in Hong Kong was the first known instance of a purely…

On Dec. 30, 1996, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced it had licensed three DTaP vaccines for…

On Oct. 2, 1996, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed a combined Hib conjugate and hepatitis B…

On Sept. 27, 1996, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed a Haemophilus b Conjugate Vaccine (ActHIB) combined…
On Jul. 31, 1996, the diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine adsorbed (Tripedia by Aventis Pasteur)…

On Jun. 18, 1996, the International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI) was launched, calling for the speedy development of…

On Mar. 29, 1996, the second inactivated hepatitis A vaccine (Vaqta by Merck) was licensed.
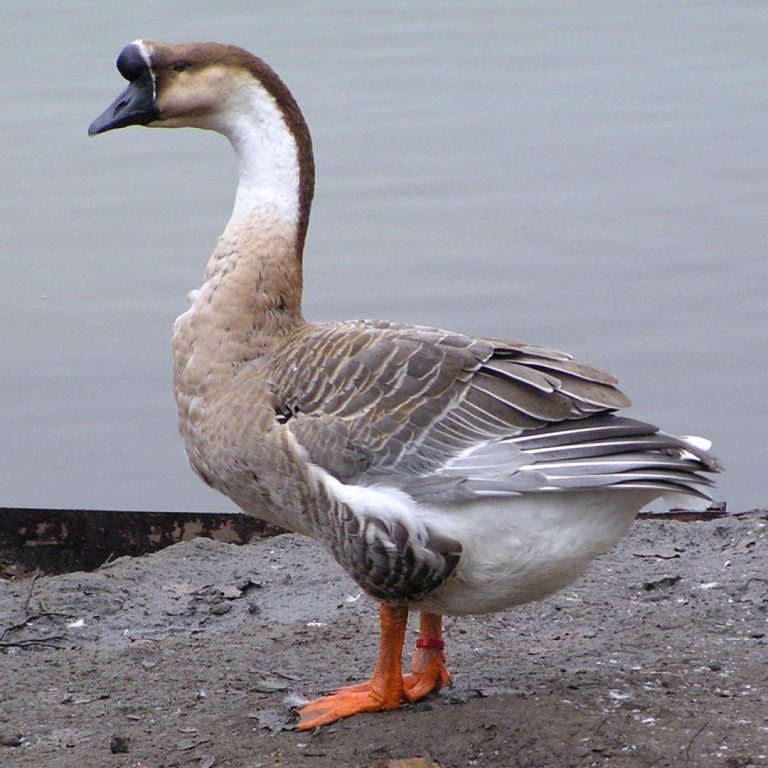

In 1996, A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996 (H5N1), the precursor of the highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza viruses (HPAIVs) was identified in…
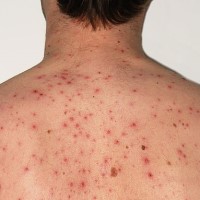
On Mar. 17, 1995, the varicella virus vaccine, live (Varivax by Merck) was licensed for the active immunization…

On Feb. 22, 1995, the first inactivated hepatitis A vaccine, distributed by SmithKline Beecham Pharmaceuticals (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), was…

In 1995, the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP), American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Association of Family…

In 1995, researchers led by Dr. Peter St. George-Hyslop at the University of Toronto discovered and cloned two…

In 1995, Hollister-Stier became Bayer Pharmaceuticals. Bayer had acquired Cutter in 1974 and Miles in 1978. Hollister-Stier Laboratories,…